+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8tva | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
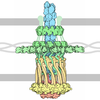
| Title | Outer Mat-T4P complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRUS / VIRUS /  Acinetobacter / SsRNA phage virus / T4P Acinetobacter / SsRNA phage virus / T4P | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvirion attachment to host cell pilus /  protein secretion by the type II secretion system / protein secretion by the type II secretion system /  type II protein secretion system complex / type II protein secretion system complex /  pilus / pilus /  virion component / virion component /  cell adhesion / cell adhesion /  membrane membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Acinetobacter phage AP205 (virus) Acinetobacter phage AP205 (virus) Acinetobacter genomosp. 16BJ (bacteria) Acinetobacter genomosp. 16BJ (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 8.55 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 8.55 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Meng, R. / Xing, Z. / Thongchol, J. / Zhang, J. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis of Acinetobacter type IV pili targeting by an RNA virus. Authors: Ran Meng / Zhongliang Xing / Jeng-Yih Chang / Zihao Yu / Jirapat Thongchol / Wen Xiao / Yuhang Wang / Karthik Chamakura / Zhiqi Zeng / Fengbin Wang / Ry Young / Lanying Zeng / Junjie Zhang /  Abstract: Acinetobacters pose a significant threat to human health, especially those with weakened immune systems. Type IV pili of acinetobacters play crucial roles in virulence and antibiotic resistance. ...Acinetobacters pose a significant threat to human health, especially those with weakened immune systems. Type IV pili of acinetobacters play crucial roles in virulence and antibiotic resistance. Single-stranded RNA bacteriophages target the bacterial retractile pili, including type IV. Our study delves into the interaction between Acinetobacter phage AP205 and type IV pili. Using cryo-electron microscopy, we solve structures of the AP205 virion with an asymmetric dimer of maturation proteins, the native Acinetobacter type IV pili bearing a distinct post-translational pilin cleavage, and the pili-bound AP205 showing its maturation proteins adapted to pilin modifications, allowing each phage to bind to one or two pili. Leveraging these results, we develop a 20-kilodalton AP205-derived protein scaffold targeting type IV pili in situ, with potential for research and diagnostics. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8tva.cif.gz 8tva.cif.gz | 521.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8tva.ent.gz pdb8tva.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8tva.json.gz 8tva.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tv/8tva https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tv/8tva ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tv/8tva ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tv/8tva | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41635MC  8tobC  8tocC  8tv9C  8tw2C  8twcC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 61063.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Acinetobacter phage AP205 (virus) / References: UniProt: Q9AZ43 Acinetobacter phage AP205 (virus) / References: UniProt: Q9AZ43 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 7470.747 Da / Num. of mol.: 20 / Fragment: residues 9-78 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Acinetobacter genomosp. 16BJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: N9RQW9 Acinetobacter genomosp. 16BJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: N9RQW9#3: Protein | Mass: 6999.778 Da / Num. of mol.: 20 / Fragment: residues 79-147 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Acinetobacter genomosp. 16BJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: N9RQW9 Acinetobacter genomosp. 16BJ (bacteria) / References: UniProt: N9RQW9 |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Acinetobacter phage AP205 / Type: VIRUS / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.378 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Acinetobacter phage AP205 (virus) Acinetobacter phage AP205 (virus) | |||||||||||||||
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: YES / Isolate: SPECIES / Type: VIRION | |||||||||||||||
| Natural host | Organism: Acinetobacter genomosp. 16BJ | |||||||||||||||
| Virus shell | Name: Coat Capsid / Diameter: 290 nm / Triangulation number (T number): 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: 20mM Tris-HCl, 150mM NaCl, pH 8.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES / Details: AP205 virion particle : YES / Details: AP205 virion particle | |||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: 3uL sample applied to a 300-mesh 2/1 copper grid |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 8.55 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 16000 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj