[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7mi8: Signal subtracted reconstruction of AAA5 and AAA6 domains of dyne... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7mi8 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
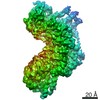
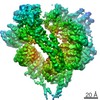
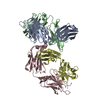
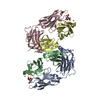
| Title | Signal subtracted reconstruction of AAA5 and AAA6 domains of dynein in the presence of a pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-based compound, Model 5 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Fusion protein of Dynein and Endolysin | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  MOTOR PROTEIN / MOTOR PROTEIN /  AAA ATPase / ATPase inhibitor AAA ATPase / ATPase inhibitor | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding /  spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding ... spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding ... karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding /  spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / viral release from host cell by cytolysis / Neutrophil degranulation / peptidoglycan catabolic process / mitotic spindle organization / cell wall macromolecule catabolic process / spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / viral release from host cell by cytolysis / Neutrophil degranulation / peptidoglycan catabolic process / mitotic spindle organization / cell wall macromolecule catabolic process /  lysozyme / lysozyme /  lysozyme activity / lysozyme activity /  cell cortex / host cell cytoplasm / defense response to bacterium / cell cortex / host cell cytoplasm / defense response to bacterium /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Santarossa, C.C. / Coudray, N. / Urnavicius, L. / Ekiert, D.C. / Bhabha, G. / Kapoor, T.M. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2021Title: Targeting allostery in the Dynein motor domain with small molecule inhibitors. Authors: Cristina C Santarossa / Keith J Mickolajczyk / Jonathan B Steinman / Linas Urnavicius / Nan Chen / Yasuhiro Hirata / Yoshiyuki Fukase / Nicolas Coudray / Damian C Ekiert / Gira Bhabha / Tarun M Kapoor /  Abstract: Cytoplasmic dyneins are AAA (ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities) motor proteins responsible for microtubule minus-end-directed intracellular transport. Dynein's unusually large size, ...Cytoplasmic dyneins are AAA (ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities) motor proteins responsible for microtubule minus-end-directed intracellular transport. Dynein's unusually large size, four distinct nucleotide-binding sites, and conformational dynamics pose challenges for the design of potent and selective chemical inhibitors. Here we use structural approaches to develop a model for the inhibition of a well-characterized S. cerevisiae dynein construct by pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-based compounds. These data, along with functional assays of dynein motility and mutagenesis studies, suggest that the compounds inhibit dynein by engaging the regulatory ATPase sites in the AAA3 and AAA4 domains, and not by interacting with dynein's main catalytic site in the AAA1 domain. A double Walker B mutation of the AAA3 and AAA4 sites substantially reduces enzyme activity, suggesting that targeting these regulatory domains is sufficient to inhibit dynein. Our findings reveal how chemical inhibitors can be designed to disrupt allosteric communication across dynein's AAA domains. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7mi8.cif.gz 7mi8.cif.gz | 261.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7mi8.ent.gz pdb7mi8.ent.gz | 181.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7mi8.json.gz 7mi8.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mi/7mi8 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mi/7mi8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mi/7mi8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mi/7mi8 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 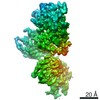 23842MC  7mi1C 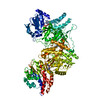 7mi3C 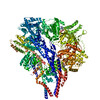 7mi6C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Mass: 304889.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast), (gene. exp.) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast), (gene. exp.)   Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus)Gene: DYN1, DHC1, YKR054C / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / Strain (production host): VY972 / References: UniProt: P36022, UniProt: P00720 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / Strain (production host): VY972 / References: UniProt: P36022, UniProt: P00720 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Dynein motor domain in the presence of a pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-based compound Motor protein Motor proteinType: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.3 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / Strain: VY972 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / Strain: VY972 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1300 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3700 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1300 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3700 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm : 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 44 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 4893 |
| Image scans | Width: 7420 / Height: 7676 / Movie frames/image: 50 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.17.1_3660: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 128004 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 7MI1 Pdb chain-ID: A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj















