[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7mi1: X-ray structure of yeast dynein motor domain in the presence of a... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7mi1 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
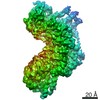
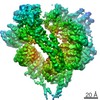
| Title | X-ray structure of yeast dynein motor domain in the presence of a pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-based compound (compound 20) | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Chimera protein of Dynein and Endolysin | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  MOTOR PROTEIN / MOTOR PROTEIN /  AAA ATPase / ATPase inhibitor AAA ATPase / ATPase inhibitor | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding /  spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding ... spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding ... karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding /  spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / viral release from host cell by cytolysis / Neutrophil degranulation / peptidoglycan catabolic process / mitotic spindle organization / cell wall macromolecule catabolic process / spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / viral release from host cell by cytolysis / Neutrophil degranulation / peptidoglycan catabolic process / mitotic spindle organization / cell wall macromolecule catabolic process /  lysozyme / lysozyme /  lysozyme activity / lysozyme activity /  cell cortex / host cell cytoplasm / defense response to bacterium / cell cortex / host cell cytoplasm / defense response to bacterium /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) | |||||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 4.5 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Santarossa, C.C. / Ekiert, D.C. / Bhabha, G. / Kapoor, T.M. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2021Title: Targeting allostery in the Dynein motor domain with small molecule inhibitors. Authors: Cristina C Santarossa / Keith J Mickolajczyk / Jonathan B Steinman / Linas Urnavicius / Nan Chen / Yasuhiro Hirata / Yoshiyuki Fukase / Nicolas Coudray / Damian C Ekiert / Gira Bhabha / Tarun M Kapoor /  Abstract: Cytoplasmic dyneins are AAA (ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities) motor proteins responsible for microtubule minus-end-directed intracellular transport. Dynein's unusually large size, ...Cytoplasmic dyneins are AAA (ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities) motor proteins responsible for microtubule minus-end-directed intracellular transport. Dynein's unusually large size, four distinct nucleotide-binding sites, and conformational dynamics pose challenges for the design of potent and selective chemical inhibitors. Here we use structural approaches to develop a model for the inhibition of a well-characterized S. cerevisiae dynein construct by pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-based compounds. These data, along with functional assays of dynein motility and mutagenesis studies, suggest that the compounds inhibit dynein by engaging the regulatory ATPase sites in the AAA3 and AAA4 domains, and not by interacting with dynein's main catalytic site in the AAA1 domain. A double Walker B mutation of the AAA3 and AAA4 sites substantially reduces enzyme activity, suggesting that targeting these regulatory domains is sufficient to inhibit dynein. Our findings reveal how chemical inhibitors can be designed to disrupt allosteric communication across dynein's AAA domains. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7mi1.cif.gz 7mi1.cif.gz | 1.8 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7mi1.ent.gz pdb7mi1.ent.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7mi1.json.gz 7mi1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mi/7mi1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mi/7mi1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mi/7mi1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mi/7mi1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mi3C  7mi6C  7mi8C  4ai6S S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Mass: 304889.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast), (gene. exp.) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast), (gene. exp.)   Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus)Gene: DYN1, DHC1, YKR054C, e, T4Tp126 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / Strain (production host): VY972 / References: UniProt: P36022, UniProt: D9IEF7 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / Strain (production host): VY972 / References: UniProt: P36022, UniProt: D9IEF7 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.17 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 61.19 % / Description: Flat and clear |
|---|---|
Crystal grow | Temperature: 291.15 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop Details: 100 mM Bis-Tris pH 6.9, 200 mM sodium acetate, 12% PEG 3350, and 10 mM TCEP |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  NSLS-II NSLS-II  / Beamline: 17-ID-2 / Wavelength: 0.92009 Å / Beamline: 17-ID-2 / Wavelength: 0.92009 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jul 31, 2018 |
| Radiation | Monochromator: horizontal bounce Si 111 double crystal monochromator Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength : 0.92009 Å / Relative weight: 1 : 0.92009 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 4.5→47.66 Å / Num. obs: 23226 / % possible obs: 99.5 % / Redundancy: 6.8 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 183.01 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.995 / Net I/σ(I): 5.99 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 4.5→4.77 Å / Redundancy: 6.5 % / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 1.13 / CC1/2: 0.484 / % possible all: 98.3 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure : :  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 4AI6 Resolution: 4.5→47.66 Å / SU ML: 0.9176 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 37.3123 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 207.43 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 4.5→47.66 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Origin x: 45.6099861602 Å / Origin y: 52.0343880284 Å / Origin z: 29.0908856623 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group | Selection details: all |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj















