[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-23841: Yeast dynein motor domain in the presence of a pyrazolo-pyrimidin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23841 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
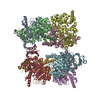
| Title | Yeast dynein motor domain in the presence of a pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-based compound, Map 1 Motor protein Motor protein | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding /  spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding ... spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding ... karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / karyogamy / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / astral microtubule / nuclear migration along microtubule / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding /  spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / viral release from host cell by cytolysis / Neutrophil degranulation / peptidoglycan catabolic process / mitotic spindle organization / cell wall macromolecule catabolic process / spindle pole body / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / viral release from host cell by cytolysis / Neutrophil degranulation / peptidoglycan catabolic process / mitotic spindle organization / cell wall macromolecule catabolic process /  lysozyme / lysozyme /  lysozyme activity / lysozyme activity /  cell cortex / host cell cytoplasm / defense response to bacterium / cell cortex / host cell cytoplasm / defense response to bacterium /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |||||||||||||||
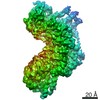
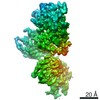
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Santarossa CC / Urnavicius L / Coudray N / Ekeirt DC / Bhabha G / Kapoor TM | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2021Title: Targeting allostery in the Dynein motor domain with small molecule inhibitors. Authors: Cristina C Santarossa / Keith J Mickolajczyk / Jonathan B Steinman / Linas Urnavicius / Nan Chen / Yasuhiro Hirata / Yoshiyuki Fukase / Nicolas Coudray / Damian C Ekiert / Gira Bhabha / Tarun M Kapoor /  Abstract: Cytoplasmic dyneins are AAA (ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities) motor proteins responsible for microtubule minus-end-directed intracellular transport. Dynein's unusually large size, ...Cytoplasmic dyneins are AAA (ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities) motor proteins responsible for microtubule minus-end-directed intracellular transport. Dynein's unusually large size, four distinct nucleotide-binding sites, and conformational dynamics pose challenges for the design of potent and selective chemical inhibitors. Here we use structural approaches to develop a model for the inhibition of a well-characterized S. cerevisiae dynein construct by pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-based compounds. These data, along with functional assays of dynein motility and mutagenesis studies, suggest that the compounds inhibit dynein by engaging the regulatory ATPase sites in the AAA3 and AAA4 domains, and not by interacting with dynein's main catalytic site in the AAA1 domain. A double Walker B mutation of the AAA3 and AAA4 sites substantially reduces enzyme activity, suggesting that targeting these regulatory domains is sufficient to inhibit dynein. Our findings reveal how chemical inhibitors can be designed to disrupt allosteric communication across dynein's AAA domains. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23841.map.gz emd_23841.map.gz | 174.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23841-v30.xml emd-23841-v30.xml emd-23841.xml emd-23841.xml | 23.4 KB 23.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23841.png emd_23841.png | 142.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_23841_half_map_1.map.gz emd_23841_half_map_1.map.gz emd_23841_half_map_2.map.gz emd_23841_half_map_2.map.gz | 150.6 MB 150.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23841 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23841 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23841 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23841 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mi6MC  7mi1C  7mi3C  7mi8C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23841.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 190.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23841.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 190.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.518 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_23841_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_23841_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Dynein motor domain in the presence of a pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-ba...
| Entire | Name: Dynein motor domain in the presence of a pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-based compound Motor protein Motor protein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Dynein motor domain in the presence of a pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-ba...
| Supramolecule | Name: Dynein motor domain in the presence of a pyrazolo-pyrimidinone-based compound type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / Recombinant strain: VY972 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / Recombinant strain: VY972 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 0.3 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Fusion protein of Dynein and Endolysin
| Macromolecule | Name: Fusion protein of Dynein and Endolysin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 304.889875 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Sequence | String: GEFVIEKSLN RIKKFWKEAQ YEVIEHSSGL KLVREWDVLE QACKEDLEEL VSMKASNYYK IFEQDCLDLE SKLTKLSEIQ VNWVEVQFY WLDLYGILGE NLDIQNFLPL ETSKFKSLTS EYKMITTRAF QLDTTIEVIH IPNFDTTLKL TIDSLKMIKS S LSTFLERQ ...String: GEFVIEKSLN RIKKFWKEAQ YEVIEHSSGL KLVREWDVLE QACKEDLEEL VSMKASNYYK IFEQDCLDLE SKLTKLSEIQ VNWVEVQFY WLDLYGILGE NLDIQNFLPL ETSKFKSLTS EYKMITTRAF QLDTTIEVIH IPNFDTTLKL TIDSLKMIKS S LSTFLERQ RRQFPRFYFL GNDDLLKIIG SGKHHDQVSK FMKKMFGSIE SIIFLEDFIT GVRSVEGEVL NLNEKIELKD SI QAQEWLN ILDTEIKLSV FTQFRDCLGQ LKDGTDIEVV VSKYIFQAIL LSAQVMWTEL VEKCLQTNQF SKYWKEVDMK IKG LLDKLN KSSDNVKKKI EALLVEYLHF NNVIGQLKNC STKEEARLLW AKVQKFYQKN DTLDDLNSVF ISQSGYLLQY KFEY IGIPE RLIYTPLLLI GFATLTDSLH QKYGGCFFGP AGTGKTETVK AFGQNLGRVV VVFNCDDSFD YQVLSRLLVG ITQIG AWGC FDQFNRLDEK VLSAVSANIQ QIQNGLQVGK SHITLLEEET PLSPHTAVFI TLNPGYNGRS ELPENLKKSF REFSMK SPQ SGTIAEMILQ IMGFEDSKSL ASKIVHFLEL LSSKCSSMNH YHFGLRTLKG VLRNCSPLIS EFGEGEKTVV ESLKRVI LP SLGDTDELVF KDELSKIFDS AGTPLNSKAI VQCLKDAGQR SGFSMSEEFL KKCMQFYYMQ KTQQALILVG KAGCGKTA T WKTVIDAMAI FDGHANVVYV IDTKVLTKES LYGSMLKATL EWRDGLFTSI LRRVNDDITG TFKNSRIWVV FDSDLDPEY VEAMNSVLDD NKILTLPNGE RLPIPPNFRI LFETDNLDHT TPATITRCGL LWFSTDVCSI SSKIDHLLNK SYEALDNKLS MFELDKLKD LISDSFDMAS LTNIFTCSND LVHILGVRTF NKLETAVQLA VHLISSYRQW FQNLDDKSLK DVITLLIKRS L LYALAGDS TGESQRAFIQ TINTYFGHDS QELSDYSTIV IANDKLSFSS FCSEIPSVSL EAHEVMRPDI VIPTIDTIKH EK IFYDLLN SKRGIILCGP PGSGKTMIMN NALRNSSLYD VVGINFSKDT TTEHILSALH RHTNYVTTSK GLTLLPKSDI KNL VLFCDE INLPKLDKYG SQNVVLFLRQ LMEKQGFWKT PENKWVTIER IHIVGACNPP TDPGRIPMSE RFTRHAAILY LGYP SGKSL SQIYEIYYKA IFKLVPEFRS YTEPFARASV HLYNECKARY STGLQSHYLF SPRELTRLVR GVYTAINTGP RQTLR SLIR LWAYEAWRIF ADRLVGVKEK NSFEQLLYET VDKYLPNQDL GNISSTSLLF SGLLSLDFKE VNKTDLVNFI EERFKT FCD EELEVPMVIH ESMVDHILRI DRALKQVQGH MMLIGASRTG KTILTRFVAW LNGLKIVQPK IHRHSNLSDF DMILKKA IS DCSLKESRTC LIIDESNILE TAFLERMNTL LANADIPDLF QGEEYDKLLN NLRNKTRSLG LLLDTEQELY DWFVGEIA K NLHVVFTICD PTNNKSSAMI SSPALFNRCI INWMGDWDTK TMSQVANNMV DVIPMEFTDF IVPEVNKELV FTEPIQTIR DAVVNILIHF DRNFYQKMKV GVNPRSPGYF IDGLRALVKL VTAKYQDLQE NQRFVNVGLE KLNESVLKVN ELNKTLGSGS GSNIFEMLR IDEGLRLKIY KDTEGYYTIG IGHLLTKSPS LNAAKSELDK AIGRNTNGVI TKDEAEKLFN QDVDAAVRGI L RNAKLKPV YDSLDAVRRA ALINMVFQMG ETGVAGFTNS LRMLQQKRWD EAAVNLAKSR WYNQTPNRAK RVITTFRTGT WD AYGSGSG SSISLVKSLT FEKERWLNTT KQFSKTSQEL IGNCIISSIY ETYFGHLNER ERADMLVILK RLLGKFAVKY DVN YRFIDY LVTLDEKMKW LECGLDKNDY FLENMSIVMN SQDAVPFLLD PSSHMITVIS NYYGNKTVLL SFLEEGFVKR LENA IRFGS VVIIQDGEFF DPIISRLISR EFNHAGNRVT VEIGDHEVDV SGDFKLFIHS CDPSGDIPIF LRSRVRLVHF VTNKE SIET RIFDITLTEE NAEMQRKRED LIKLNTEYKL KLKNLEKRLL EELNNSQGNM LENDELMVTL NNLKKEAMNI EKKLSE SEE FFPQFDNLVE EYSIIGKHSV KIFSMLEKFG QFHWFYGISI GQFLSCFKRV FIKKSRETRA ARTRVDEILW LLYQEVY CQ FSTALDKKFK MIMAMTMFCL YKFDIESEQY KEAVLTMIGV LSESSDGVPK LTVDTNDDLR YLWDYVTTKS YISALNWF K NEFFVDEWNI ADVVANSENN YFTMASERDV DGTFKLIELA KASKESLKII PLGSIENLNY AQEEISKSKI EGGWILLQN IQMSLSWVKT YLHKHVEETK AAEEHEKFKM FMTCHLTGDK LPAPLLQRTD RVVYEDIPGI LDTVKDLWGS QFFTGKISGV WSVYCTFLL SWFHALITAR TRLVPHGFSK KYYFNDCDFQ FASVYLENVL ATNSTNNIPW AQVRDHIATI VYGGKIDEEK D LEVVAKLC AHVFCGSDNL QIVPGVRIPQ PLLQQSEEEE RARLTAILSN TIEPADSLSS WLQLPRESIL DYERLQAKEV AS STEQLLQ EMGSGSGSHH HHHH |
-Macromolecule #2: (8S)-6-(3-bromophenoxy)-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclopropyl]-7-hydro...
| Macromolecule | Name: (8S)-6-(3-bromophenoxy)-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclopropyl]-7-hydroxypyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carbonitrile type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ZG7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 481.729 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ZG7: |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information | 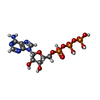 ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.039 kPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated defocus max: 3.7 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 1.3 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 7420 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 7676 pixel / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 4893 / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 44.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Software - Name: CTFFIND (ver. 4.1) |
|---|---|
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3.0) |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3.0) |
| Final reconstruction | Number classes used: 2 / Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3.0) / Number images used: 136180 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z
Z Y
Y X
X