+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Mechanism of actin-dependent activation of nucleotidyl cyclase toxins from bacterial human pathogens. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 12, Issue 1, Page 6628, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Nov 16, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Alexander Belyy / Felipe Merino / Undine Mechold / Stefan Raunser /   |
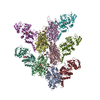
| PubMed Abstract | Bacterial human pathogens secrete initially inactive nucleotidyl cyclases that become potent enzymes by binding to actin inside eukaryotic host cells. The underlying molecular mechanism of this ...Bacterial human pathogens secrete initially inactive nucleotidyl cyclases that become potent enzymes by binding to actin inside eukaryotic host cells. The underlying molecular mechanism of this activation is, however, unclear. Here, we report structures of ExoY from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Vibrio vulnificus bound to their corresponding activators F-actin and profilin-G-actin. The structures reveal that in contrast to the apo-state, two flexible regions become ordered and interact strongly with actin. The specific stabilization of these regions results in an allosteric stabilization of the nucleotide binding pocket and thereby to an activation of the enzyme. Differences in the sequence and conformation of the actin-binding regions are responsible for the selective binding to either F- or G-actin. Other nucleotidyl cyclase toxins that bind to calmodulin rather than actin undergo a similar disordered-to-ordered transition during activation, suggesting that the allosteric activation-by-stabilization mechanism of ExoY is conserved in these enzymes, albeit the different activator. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:34785651 / PubMed:34785651 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.2 - 4.2 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-13158, PDB-7p1g: EMDB-13159, PDB-7p1h:  EMDB-13160: |
| Chemicals | 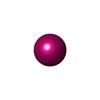 ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-GH3: 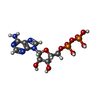 ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-PO4:  ChemComp-CA:  ChemComp-ATP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  TOXIN / TOXIN /  Bacterial toxin / Bacterial toxin /  F-actin / G-actin / F-actin / G-actin /  profilin profilin |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers