+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8s3e | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of rabbit Slo1 in complex with gamma1/LRRC26 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  MEMBRANE PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN /  Ion channel / potassium transport Ion channel / potassium transport | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmonoatomic ion-gated channel activity / monoatomic ion channel complex /  potassium channel activity / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / potassium channel activity / endoplasmic reticulum membrane /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.39 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.39 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Redhardt, M. / Raunser, S. / Raisch, T. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: FEBS Lett / Year: 2024 Journal: FEBS Lett / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM structure of the Slo1 potassium channel with the auxiliary γ1 subunit suggests a mechanism for depolarization-independent activation. Authors: Milena Redhardt / Stefan Raunser / Tobias Raisch /  Abstract: Mammalian Ca-dependent Slo K channels can stably associate with auxiliary γ subunits which fundamentally alter their behavior. By a so far unknown mechanism, the four γ subunits reduce the need for ...Mammalian Ca-dependent Slo K channels can stably associate with auxiliary γ subunits which fundamentally alter their behavior. By a so far unknown mechanism, the four γ subunits reduce the need for voltage-dependent activation and, thereby, allow Slo to open independently of an action potential. Here, using cryo-EM, we reveal how the transmembrane helix of γ1/LRRC26 binds and presumably stabilizes the activated voltage-sensor domain of Slo1. The activation is further enhanced by an intracellular polybasic stretch which locally changes the charge gradient across the membrane. Our data provide a possible explanation for Slo1 regulation by the four γ subunits and also their different activation efficiencies. This suggests a novel activation mechanism of voltage-gated ion channels by auxiliary subunits. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8s3e.cif.gz 8s3e.cif.gz | 808.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8s3e.ent.gz pdb8s3e.ent.gz | 645.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8s3e.json.gz 8s3e.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s3/8s3e https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s3/8s3e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s3/8s3e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/s3/8s3e | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 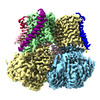 19691MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 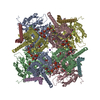
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 8 molecules ABCDEFGH
| #1: Protein |  / BK channel / BKCA alpha / Calcium-activated potassium channel / subfamily M subunit alpha-1 / K(VCA) ...BK channel / BKCA alpha / Calcium-activated potassium channel / subfamily M subunit alpha-1 / K(VCA)alpha / KCa1.1 / Maxi K channel / MaxiK / Slo-alpha / Slo1 / Slowpoke homolog / RbSlo / Slo homolog / BK channel / BKCA alpha / Calcium-activated potassium channel / subfamily M subunit alpha-1 / K(VCA) ...BK channel / BKCA alpha / Calcium-activated potassium channel / subfamily M subunit alpha-1 / K(VCA)alpha / KCa1.1 / Maxi K channel / MaxiK / Slo-alpha / Slo1 / Slowpoke homolog / RbSlo / Slo homologMass: 126029.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Gene: KCNMA1, KCNMA / Production host: Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Gene: KCNMA1, KCNMA / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BG98 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BG98#2: Protein | Mass: 35938.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Production host: Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 6 types, 81 molecules 





| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-CLR /  Cholesterol Cholesterol#4: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-6PL / ( #6: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #7: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #8: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |  Water Water |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Slo1-gamma1 complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 52.3 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.39 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 826667 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj










