[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7ums: Structure of the VP5*/VP8* assembly from the human rotavirus stra... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ums | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the VP5*/VP8* assembly from the human rotavirus strain CDC-9 in complex with antibody 41 - Upright conformation | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRUS / VIRUS /  Rotavirus / Rotavirus /  human / CDC-9 / VP4 / VP5* / VP8* / antibody #41 / broadly neutralizing / human / CDC-9 / VP4 / VP5* / VP8* / antibody #41 / broadly neutralizing /  cryo-EM cryo-EM | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationviral intermediate capsid / host cell endoplasmic reticulum lumen / T=13 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell rough endoplasmic reticulum / host cytoskeleton / viral outer capsid / permeabilization of host organelle membrane involved in viral entry into host cell / symbiont entry into host cell via permeabilization of inner membrane / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / membrane => GO:0016020 ...viral intermediate capsid / host cell endoplasmic reticulum lumen / T=13 icosahedral viral capsid / host cell rough endoplasmic reticulum / host cytoskeleton / viral outer capsid / permeabilization of host organelle membrane involved in viral entry into host cell / symbiont entry into host cell via permeabilization of inner membrane / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / membrane => GO:0016020 / host cell surface receptor binding / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane /  viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / structural molecule activity / viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / structural molecule activity /  membrane / membrane /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Rotavirus Rotavirus  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Jenni, S. / Zongli, L. / Wang, Y. / Bessey, T. / Salgado, E.N. / Schmidt, A.G. / Greenberg, H.B. / Jiang, B. / Harrison, S.C. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2022 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2022Title: Rotavirus VP4 Epitope of a Broadly Neutralizing Human Antibody Defined by Its Structure Bound with an Attenuated-Strain Virion. Authors: Simon Jenni / Zongli Li / Yuhuan Wang / Theresa Bessey / Eric N Salgado / Aaron G Schmidt / Harry B Greenberg / Baoming Jiang / Stephen C Harrison /  Abstract: Rotavirus live-attenuated vaccines, both mono- and pentavalent, generate broadly heterotypic protection. B-cells isolated from adults encode neutralizing antibodies, some with affinity for VP5*, that ...Rotavirus live-attenuated vaccines, both mono- and pentavalent, generate broadly heterotypic protection. B-cells isolated from adults encode neutralizing antibodies, some with affinity for VP5*, that afford broad protection in mice. We have mapped the epitope of one such antibody by determining the high-resolution cryo-EM structure of its antigen-binding fragment (Fab) bound to the virion of a candidate vaccine strain, CDC-9. The Fab contacts both the distal end of a VP5* β-barrel domain and the two VP8* lectin-like domains at the tip of a projecting spike. Its interactions with VP8* do not impinge on the likely receptor-binding site, suggesting that the mechanism of neutralization is at a step subsequent to initial attachment. We also examined structures of CDC-9 virions from two different stages of serial passaging. Nearly all the VP4 (cleaved to VP8*/VP5*) spikes on particles from the earlier passage (wild-type isolate) had transitioned from the "upright" conformation present on fully infectious virions to the "reversed" conformation that is probably the end state of membrane insertion, unable to mediate penetration, consistent with the very low infectivity of the wild-type isolate. About half the VP4 spikes were upright on particles from the later passage, which had recovered substantial infectivity but had acquired an attenuated phenotype in neonatal rats. A mutation in VP4 that occurred during passaging appears to stabilize the interface at the apex of the spike and could account for the greater stability of the upright spikes on the late-passage, attenuated isolate. Rotavirus live-attenuated vaccines generate broadly heterotypic protection, and B-cells isolated from adults encode antibodies that are broadly protective in mice. Determining the structural and mechanistic basis of broad protection can contribute to understanding the current limitations of vaccine efficacy in developing countries. The structure of an attenuated human rotavirus isolate (CDC-9) bound with the Fab fragment of a broadly heterotypic protective antibody shows that protection is probably due to inhibition of the conformational transition in the viral spike protein (VP4) critical for viral penetration, rather than to inhibition of receptor binding. A comparison of structures of CDC-9 virus particles at two stages of serial passaging supports a proposed mechanism for initial steps in rotavirus membrane penetration. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ums.cif.gz 7ums.cif.gz | 4.7 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ums.ent.gz pdb7ums.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ums.json.gz 7ums.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/7ums https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/7ums ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/7ums ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/7ums | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  26608MC  7umtC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Outer capsid protein ... , 2 types, 6 molecules TUV123
| #1: Protein | Mass: 26248.848 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rotavirus / Strain: CDC-9 Rotavirus / Strain: CDC-9Gene: VP4, W907_45309gpVP4, W907_45314gpVP4, W907_45315gpVP4, W907_45321gpVP4, W907_45328gpVP4, W907_45346gpVP4 Production host:   Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) / References: UniProt: X4YMN0 Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) / References: UniProt: X4YMN0#2: Protein | Mass: 59605.254 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rotavirus / Strain: CDC-9 Rotavirus / Strain: CDC-9Gene: VP4, W907_45309gpVP4, W907_45314gpVP4, W907_45315gpVP4, W907_45321gpVP4, W907_45328gpVP4, W907_45346gpVP4 Production host:   Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) / References: UniProt: X4YMN0 Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) / References: UniProt: X4YMN0 |
|---|
-Protein , 2 types, 36 molecules ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRabcdefghijkl...
| #5: Protein | Mass: 44994.965 Da / Num. of mol.: 18 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rotavirus / Strain: CDC-9 / Gene: VP6 / Production host: Rotavirus / Strain: CDC-9 / Gene: VP6 / Production host:   Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) / References: UniProt: A0A223GHC7 Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) / References: UniProt: A0A223GHC7#6: Protein | Mass: 37435.934 Da / Num. of mol.: 18 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Rotavirus / Strain: CDC-9 Rotavirus / Strain: CDC-9Gene: VP7, NC78_51708gpVP7, NC78_52349gpVP7, NC78_52352gpVP7, NC78_52353gpVP7, NC78_52354gpVP7, NC78_52356gpVP7, NC78_52357gpVP7b, W907_45360gpVP7, W907_45361gpVP7, W907_45368gpVP7 Production host:   Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) / References: UniProt: B1NP55 Chlorocebus aethiops (grivet) / References: UniProt: B1NP55 |
|---|
-Antibody , 2 types, 4 molecules 4657
| #3: Antibody |  Fragment antigen-binding Fragment antigen-bindingMass: 25386.260 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)#4: Antibody |  Fragment antigen-binding Fragment antigen-bindingMass: 23322.598 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): HEK293 / Production host:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|
-Sugars , 2 types, 36 molecules 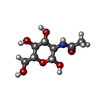
| #7: Polysaccharide | beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta- ...beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / Mass: 586.542 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mass: 586.542 Da / Num. of mol.: 1Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
|---|---|
| #8: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG /  N-Acetylglucosamine N-Acetylglucosamine |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 72 molecules 
| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: STRAIN / Type: VIRION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 422920 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 83.33 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj









