[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-37476: Human L-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.2 (Class II) in t... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human L-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.2 (Class II) in the presence of pinaverium at 3.2 Angstrom resolution | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  Cav1.2 / Channels / Calcium Ion-Selective / Cav1.2 / Channels / Calcium Ion-Selective /  TRANSPORT PROTEIN / TRANSPORT PROTEIN /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information : / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / : / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential /  immune system development / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential ... immune system development / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential ... : / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / : / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential /  immune system development / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity / cardiac conduction / immune system development / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity / cardiac conduction /  L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / camera-type eye development / NCAM1 interactions / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / embryonic forelimb morphogenesis / calcium ion transport into cytosol / cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / camera-type eye development / NCAM1 interactions / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / embryonic forelimb morphogenesis / calcium ion transport into cytosol / cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel /  voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuronal dense core vesicle / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / alpha-actinin binding / regulation of calcium ion transport / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuronal dense core vesicle / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / alpha-actinin binding / regulation of calcium ion transport / calcium ion import across plasma membrane /  voltage-gated calcium channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion /  sarcoplasmic reticulum / Regulation of insulin secretion / calcium ion transmembrane transport / postsynaptic density membrane / Z disc / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / cellular response to amyloid-beta / calcium ion transport / sarcoplasmic reticulum / Regulation of insulin secretion / calcium ion transmembrane transport / postsynaptic density membrane / Z disc / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / cellular response to amyloid-beta / calcium ion transport /  heart development / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / heart development / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration /  perikaryon / perikaryon /  postsynaptic density / postsynaptic density /  calmodulin binding / calmodulin binding /  dendrite / extracellular exosome / dendrite / extracellular exosome /  membrane / membrane /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gao S / Yao X / Fan X / Yan N | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis for human Ca1.2 inhibition by multiple drugs and the neurotoxin calciseptine. Authors: Shuai Gao / Xia Yao / Jiaofeng Chen / Gaoxingyu Huang / Xiao Fan / Lingfeng Xue / Zhangqiang Li / Tong Wu / Yupeng Zheng / Jian Huang / Xueqin Jin / Yan Wang / Zhifei Wang / Yong Yu / Lei ...Authors: Shuai Gao / Xia Yao / Jiaofeng Chen / Gaoxingyu Huang / Xiao Fan / Lingfeng Xue / Zhangqiang Li / Tong Wu / Yupeng Zheng / Jian Huang / Xueqin Jin / Yan Wang / Zhifei Wang / Yong Yu / Lei Liu / Xiaojing Pan / Chen Song / Nieng Yan /   Abstract: Ca1.2 channels play crucial roles in various neuronal and physiological processes. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of human Ca1.2, both in its apo form and in complex with several drugs, as well ...Ca1.2 channels play crucial roles in various neuronal and physiological processes. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of human Ca1.2, both in its apo form and in complex with several drugs, as well as the peptide neurotoxin calciseptine. Most structures, apo or bound to calciseptine, amlodipine, or a combination of amiodarone and sofosbuvir, exhibit a consistent inactivated conformation with a sealed gate, three up voltage-sensing domains (VSDs), and a down VSD. Calciseptine sits on the shoulder of the pore domain, away from the permeation path. In contrast, when pinaverium bromide, an antispasmodic drug, is inserted into a cavity reminiscent of the IFM-binding site in Na channels, a series of structural changes occur, including upward movement of VSD coupled with dilation of the selectivity filter and its surrounding segments in repeat III. Meanwhile, S4-5 merges with S5 to become a single helix, resulting in a widened but still non-conductive intracellular gate. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_37476.map.gz emd_37476.map.gz | 79 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-37476-v30.xml emd-37476-v30.xml emd-37476.xml emd-37476.xml | 21.4 KB 21.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_37476.png emd_37476.png | 45.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-37476.cif.gz emd-37476.cif.gz | 8.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_37476_additional_1.map.gz emd_37476_additional_1.map.gz emd_37476_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37476_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37476_half_map_2.map.gz emd_37476_half_map_2.map.gz | 78.9 MB 77.7 MB 77.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37476 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37476 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37476 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37476 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8weaMC  8fhsC 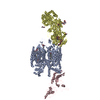 8we6C  8we7C 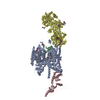 8we8C  8we9C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_37476.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_37476.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.114 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_37476_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_37476_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_37476_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cav1.2
| Entire | Name: Cav1.2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cav1.2
| Supramolecule | Name: Cav1.2 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 246.85125 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MVNENTRMYI PEENHQGSNY GSPRPAHANM NANAAAGLAP EHIPTPGAAL SWQAAIDAAR QAKLMGSAGN ATISTVSSTQ RKRQQYGKP KKQGSTTATR PPRALLCLTL KNPIRRACIS IVEWKPFEII ILLTIFANCV ALAIYIPFPE DDSNATNSNL E RVEYLFLI ...String: MVNENTRMYI PEENHQGSNY GSPRPAHANM NANAAAGLAP EHIPTPGAAL SWQAAIDAAR QAKLMGSAGN ATISTVSSTQ RKRQQYGKP KKQGSTTATR PPRALLCLTL KNPIRRACIS IVEWKPFEII ILLTIFANCV ALAIYIPFPE DDSNATNSNL E RVEYLFLI IFTVEAFLKV IAYGLLFHPN AYLRNGWNLL DFIIVVVGLF SAILEQATKA DGANALGGKG AGFDVKALRA FR VLRPLRL VSGVPSLQVV LNSIIKAMVP LLHIALLVLF VIIIYAIIGL ELFMGKMHKT CYNQEGIADV PAEDDPSPCA LET GHGRQC QNGTVCKPGW DGPKHGITNF DNFAFAMLTV FQCITMEGWT DVLYWVNDAV GRDWPWIYFV TLIIIGSFFV LNLV LGVLS GEFSKEREKA KARGDFQKLR EKQQLEEDLK GYLDWITQAE DIDPENEDEG MDEEKPRNMS MPTSETESVN TENVA GGDI EGENCGARLA HRISKSKFSR YWRRWNRFCR RKCRAAVKSN VFYWLVIFLV FLNTLTIASE HYNQPNWLTE VQDTAN KAL LALFTAEMLL KMYSLGLQAY FVSLFNRFDC FVVCGGILET ILVETKIMSP LGISVLRCVR LLRIFKITRY WNSLSNL VA SLLNSVRSIA SLLLLLFLFI IIFSLLGMQL FGGKFNFDEM QTRRSTFDNF PQSLLTVFQI LTGEDWNSVM YDGIMAYG G PSFPGMLVCI YFIILFICGN YILLNVFLAI AVDNLADAES LTSAQKEEEE EKERKKLART ASPEKKQELV EKPAVGESK EEKIELKSIT ADGESPPATK INMDDLQPNE NEDKSPYPNP ETTGEEDEEE PEMPVGPRPR PLSELHLKEK AVPMPEASAF FIFSSNNRF RLQCHRIVND TIFTNLILFF ILLSSISLAA EDPVQHTSFR NHILGNADYV FTSIFTLEII LKMTAYGAFL H KGSFCRNY FNILDLLVVS VSLISFGIQS SAINVVKILR VLRVLRPLRA INRAKGLKHV VQCVFVAIRT IGNIVIVTTL LQ FMFACIG VQLFKGKLYT CSDSSKQTEA ECKGNYITYK DGEVDHPIIQ PRSWENSKFD FDNVLAAMMA LFTVSTFEGW PEL LYRSID SHTEDKGPIY NYRVEISIFF IIYIIIIAFF MMNIFVGFVI VTFQEQGEQE YKNCELDKNQ RQCVEYALKA RPLR RYIPK NQHQYKVWYV VNSTYFEYLM FVLILLNTIC LAMQHYGQSC LFKIAMNILN MLFTGLFTVE MILKLIAFKP KGYFS DPWN VFDFLIVIGS IIDVILSETN HYFCDAWNTF DALIVVGSIV DIAITEVNPA EHTQCSPSMN AEENSRISIT FFRLFR VMR LVKLLSRGEG IRTLLWTFIK SFQALPYVAL LIVMLFFIYA VIGMQVFGKI ALNDTTEINR NNNFQTFPQA VLLLFRC AT GEAWQDIMLA CMPGKKCAPE SEPSNSTEGE TPCGSSFAVF YFISFYMLCA FLIINLFVAV IMDNFDYLTR DWSILGPH H LDEFKRIWAE YDPEAKGRIK HLDVVTLLRR IQPPLGFGKL CPHRVACKRL VSMNMPLNSD GTVMFNATLF ALVRTALRI KTEGNLEQAN EELRAIIKKI WKRTSMKLLD QVVPPAGDDE VTVGKFYATF LIQEYFRKFK KRKEQGLVGK PSQRNALSLQ AGLRTLHDI GPEIRRAISG DLTAEEELDK AMKEAVSAAS EDDIFRRAGG LFGNHVSYYQ SDGRSAFPQT FTTQRPLHIN K AGSSQGDT ESPSHEKLVD STFTPSSYSS TGSNANINNA NNTALGRLPR PAGYPSTVST VEGHGPPLSP AIRVQEVAWK LS SNRERHV PMCEDLELRR DSGSAGTQAH CLLLRKANPS RCHSRESQAA MAGQEETSQD ETYEVKMNHD TEACSEPSLL STE MLSYQD DENRQLTLPE EDKRDIRQSP KRGFLRSASL GRRASFHLEC LKRQKDRGGD ISQKTVLPLH LVHHQALAVA GLSP LLQRS HSPASFPRPF ATPPATPGSR GWPPQPVPTL RLEGVESSEK LNSSFPSIHC GSWAETTPGG GGSSAARRVR PVSLM VPSQ AGAPGRQFHG SASSLVEAVL ISEGLGQFAQ DPKFIEVTTQ ELADACDMTI EEMESAADNI LSGGAPQSPN GALLPF VNC RDAGQDRAGG EEDAGCVRAR GRPSEEELQD SRVYVSSL UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C |
-Macromolecule #2: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 124.692469 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAAGCLLALT LTLFQSLLIG PSSEEPFPSA VTIKSWVDKM QEDLVTLAKT ASGVNQLVDI YEKYQDLYTV EPNNARQLVE IAARDIEKL LSNRSKALVR LALEAEKVQA AHQWREDFAS NEVVYYNAKD DLDPEKNDSE PGSQRIKPVF IEDANFGRQI S YQHAAVHI ...String: MAAGCLLALT LTLFQSLLIG PSSEEPFPSA VTIKSWVDKM QEDLVTLAKT ASGVNQLVDI YEKYQDLYTV EPNNARQLVE IAARDIEKL LSNRSKALVR LALEAEKVQA AHQWREDFAS NEVVYYNAKD DLDPEKNDSE PGSQRIKPVF IEDANFGRQI S YQHAAVHI PTDIYEGSTI VLNELNWTSA LDEVFKKNRE EDPSLLWQVF GSATGLARYY PASPWVDNSR TPNKIDLYDV RR RPWYIQG AASPKDMLIL VDVSGSVSGL TLKLIRTSVS EMLETLSDDD FVNVASFNSN AQDVSCFQHL VQANVRNKKV LKD AVNNIT AKGITDYKKG FSFAFEQLLN YNVSRANCNK IIMLFTDGGE ERAQEIFNKY NKDKKVRVFT FSVGQHNYDR GPIQ WMACE NKGYYYEIPS IGAIRINTQE YLDVLGRPMV LAGDKAKQVQ WTNVYLDALE LGLVITGTLP VFNITGQFEN KTNLK NQLI LGVMGVDVSL EDIKRLTPRF TLCPNGYYFA IDPNGYVLLH PNLQPKPIGV GIPTINLRKR RPNIQNPKSQ EPVTLD FLD AELENDIKVE IRNKMIDGES GEKTFRTLVK SQDERYIDKG NRTYTWTPVN GTDYSLALVL PTYSFYYIKA KLEETIT QA RYSETLKPDN FEESGYTFIA PRDYCNDLKI SDNNTEFLLN FNEFIDRKTP NNPSCNADLI NRVLLDAGFT NELVQNYW S KQKNIKGVKA RFVVTDGGIT RVYPKEAGEN WQENPETYED SFYKRSLDND NYVFTAPYFN KSGPGAYESG IMVSKAVEI YIQGKLLKPA VVGIKIDVNS WIENFTKTSI RDPCAGPVCD CKRNSDVMDC VILDDGGFLL MANHDDYTNQ IGRFFGEIDP SLMRHLVNI SVYAFNKSYD YQSVCEPGAA PKQGAGHRSA YVPSVADILQ IGWWATAAAW SILQQFLLSL TFPRLLEAVE M EDDDFTAS LSKQSCITEQ TQYFFDNDSK SFSGVLDCGN CSRIFHGEKL MNTNLIFIMV ESKGTCPCDT RLLIQAEQTS DG PNPCDMV KQPRYRKGPD VCFDNNVLED YTDCGGVSGL NPSLWYIIGI QFLLLWLVSG STHRLL UniProtKB:  Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 |
-Macromolecule #6: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #7: (3beta,14beta,17beta,25R)-3-[4-methoxy-3-(methoxymethyl)butoxy]sp...
| Macromolecule | Name: (3beta,14beta,17beta,25R)-3-[4-methoxy-3-(methoxymethyl)butoxy]spirost-5-en type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: 9Z9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 544.805 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-9Z9: |
-Macromolecule #8: 4-[(2-bromanyl-4,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)methyl]-4-[2-[2-[(1~{R},2~{S}...
| Macromolecule | Name: 4-[(2-bromanyl-4,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)methyl]-4-[2-[2-[(1~{R},2~{S},5~{R})-6,6-dimethyl-2-bicyclo[3.1.1]heptanyl]ethoxy]ethyl]morpholin-4-ium type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: WB9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 511.512 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-WB9: |
-Macromolecule #9: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 9 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information | 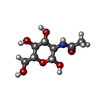 ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.9000000000000001 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.9000000000000001 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 299035 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller























 Z
Z Y
Y X
X