[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-27811: Symmetry expansion of yeast cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to Lis1 in... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 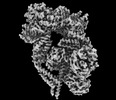 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
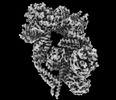
| Title | Symmetry expansion of yeast cytoplasmic dynein-1 bound to Lis1 in the chi conformation. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  dynein / dynein /  motor protein / transport motor protein / transport | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of microtubule plus-end binding / microtubule sliding / microtubule organizing center organization / nuclear migration along microtubule / vesicle transport along microtubule / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation /  dynein complex / microtubule plus-end binding / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding ...positive regulation of microtubule plus-end binding / microtubule sliding / microtubule organizing center organization / nuclear migration along microtubule / vesicle transport along microtubule / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / dynein complex / microtubule plus-end binding / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding ...positive regulation of microtubule plus-end binding / microtubule sliding / microtubule organizing center organization / nuclear migration along microtubule / vesicle transport along microtubule / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation /  dynein complex / microtubule plus-end binding / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / nuclear migration / microtubule associated complex / dynein intermediate chain binding / dynein complex binding / microtubule-based movement / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule / dynein complex / microtubule plus-end binding / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / nuclear migration / microtubule associated complex / dynein intermediate chain binding / dynein complex binding / microtubule-based movement / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / cytoplasmic microtubule /  kinetochore / kinetochore /  spindle pole / spindle pole /  nuclear envelope / nuclear envelope /  microtubule / microtubule /  cell division / cell division /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |||||||||
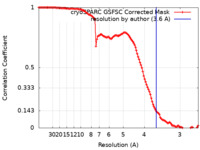
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Reimer JM / Lahiri I / Leschziner AE | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Lis1 relieves cytoplasmic dynein-1 autoinhibition by acting as a molecular wedge. Authors: Eva P Karasmanis / Janice M Reimer / Agnieszka A Kendrick / Kendrick H V Nguyen / Jennifer A Rodriguez / Joey B Truong / Indrajit Lahiri / Samara L Reck-Peterson / Andres E Leschziner /   Abstract: Cytoplasmic dynein-1 transports intracellular cargo towards microtubule minus ends. Dynein is autoinhibited and undergoes conformational changes to form an active complex that consists of one or two ...Cytoplasmic dynein-1 transports intracellular cargo towards microtubule minus ends. Dynein is autoinhibited and undergoes conformational changes to form an active complex that consists of one or two dynein dimers, the dynactin complex, and activating adapter(s). The Lissencephaly 1 gene, LIS1, is genetically linked to the dynein pathway from fungi to mammals and is mutated in people with the neurodevelopmental disease lissencephaly. Lis1 is required for active dynein complexes to form, but how it enables this is unclear. Here, we present a structure of two yeast dynein motor domains with two Lis1 dimers wedged in-between. The contact sites between dynein and Lis1 in this structure, termed 'Chi,' are required for Lis1's regulation of dynein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae in vivo and the formation of active human dynein-dynactin-activating adapter complexes in vitro. We propose that this structure represents an intermediate in dynein's activation pathway, revealing how Lis1 relieves dynein's autoinhibited state. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27811.map.gz emd_27811.map.gz | 157.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27811-v30.xml emd-27811-v30.xml emd-27811.xml emd-27811.xml | 18.9 KB 18.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27811_fsc.xml emd_27811_fsc.xml | 11.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
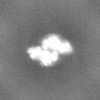
| Images |  emd_27811.png emd_27811.png | 91.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27811_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27811_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27811_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27811_half_map_2.map.gz | 154.5 MB 154.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27811 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27811 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27811 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27811 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8e00MC  8dzzC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27811.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27811.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.31 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_27811_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
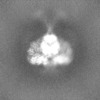
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
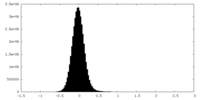
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_27811_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
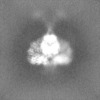
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : cytoplasmic dynein(E2448Q) bound to Lis1 in chi conformation
| Entire | Name: cytoplasmic dynein(E2448Q) bound to Lis1 in chi conformation |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: cytoplasmic dynein(E2448Q) bound to Lis1 in chi conformation
| Supramolecule | Name: cytoplasmic dynein(E2448Q) bound to Lis1 in chi conformation type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
-Macromolecule #1: Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic
| Macromolecule | Name: Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: 100% identical to UniParc UPI0005D9E17C / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 331.524 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Sequence | String: GDQLTHVVEE VKTYDLVWRS IKNLWEDVQR TFETPWCRVD VLLLQSDLAN FLRRADELPR AVKQFEMYKS LFSQVNMLTS VNKILVELK DGALKPRHWN MIFRDIGKRQ IQKNLLDKLE FSLKDVMVLN LTLNEILLTK IIERAQKEFV IEKSLNRIKK F WKEAQYEV ...String: GDQLTHVVEE VKTYDLVWRS IKNLWEDVQR TFETPWCRVD VLLLQSDLAN FLRRADELPR AVKQFEMYKS LFSQVNMLTS VNKILVELK DGALKPRHWN MIFRDIGKRQ IQKNLLDKLE FSLKDVMVLN LTLNEILLTK IIERAQKEFV IEKSLNRIKK F WKEAQYEV IEHSSGLKLV REWDVLEQAC KEDLEELVSM KASNYYKIFE QDCLDLESKL TKLSEIQVNW VEVQFYWLDL YG ILGENLD IQNFLPLETS KFKSLTSEYK MITTRAFQLD TTIEVIHIPN FDTTLKLTID SLKMIKSSLS TFLERQRRQF PRF YFLGND DLLKIIGSGK HHDQVSKFMK KMFGSIESII FFEDSITGVR SVEGEVLNLN EKIELKDSIQ AQEWLNILDT EIKL SVFTQ FRDCLGQLKD GTDIEVVVSK YIFQAILLSA QVMWTELVEK CLQTNEFSKY WKEVDMKIKG LLDKLNKSSD NVKKK IEAL LVEYLHFNNV IGQLKNCSTK EEARLLWAKV QKFYQKNDTL DDLNSVFISQ SGYLLQYKFE YIGIPERLIY TPLLLV GFA TLTDSLHQKY GGCFFGPAGT GKTETVKAFG QNLGRVVVVF NCDDSFDYQV LSRLLVGITQ IGAWGCFDEF NRLDEKV LS AVSANIQQIQ NGLQVGKSHI TLLEEETPLS PHTAVFITLN PGYNGRSELP ENLKKSFREF SMKSPQSGTI AEMILQIM G FEDSKSLASK IVHFLELLSS KCSSMNHYHF GLRTLKGVLR NCSPLVSEFG EGEKTVVESL KRVILPSLGD TDELVFKDE LSKIFDSAGT PLNSKAIVQC LKDAGQRSGF SMSEEFLKKC MQFYYMQKTQ QALILVGKAG CGKTATWKTV IDAMAIFDGH ANVVYVIDT KVLTKESLYG SMLKATLEWR DGLFTSILRR VNDDITGTFK NSRIWVVFDS DLDPEYVEAM NSVLDDNKIL T LPNGERLP IPPNFRILFE TDNLDHTTPA TITRCGLLWF STDVCSISSK IDHLLNKSYE ALDNKLSMFE LDKLKDLISD SF DMASLTN IFTCSNDLVH ILGVRTFNKL ETAVQLAVHL ISSYRQWFQN LDDKSLKDVI TLLIKRSLLY ALAGDSTGES QRA FIQTIN TYFGHDSQEL SDYSTIVIAN DKLSFSSFCS EIPSVSLEAH EVMRPDIVIP TIDTIKHEKI FYDLLNSKRG IILC GPPGS GKTMIMNNAL RNSSLYDVVG INFSKDTTTE HILSALHRHT NYVTTSKGLT LLPKSDIKNL VLFCDQINLP KLDKY GSQN VVLFLRQLME KQGFWKTPEN KWVTIERIHI VGACNPPTDP GRIPMSERFT RHAAILYLGY PSGKSLSQIY EIYYKA IFK LVPEFRSYTE PFARASVHLY NECKARYSTG LQSHYLFSPR ELTRLVRGVY TAINTGPRQT LRSLIRLWAY EAWRIFA DR LVGVKEKNSF EQLLYETVDK YLPNQDLGNI SSTSLLFSGL LSLDFKEVNK TDLVNFIEER FKTFCDEELE VPMVIHES M VDHILRIDRA LKQVQGHMML IGASRTGKTI LTRFVAWLNG LKIVQPKIHR HSNLSDFDMI LKKAISDCSL KESRTCLII DESNILETAF LERMNTLLAN ADIPDLFQGE EYDKLLNNLR NKTRSLGLLL DTEQELYDWF VGEIAKNLHV VFTICDPTNN KSSAMISSP ALFNRCIINW MGDWDTKTMS QVANNMVDVV PMEFTDFIVP EVNKELVFTE PIQTIRDAVV NILIHFDRNF Y QKMKVGVN PRSPGYFIDG LRALVKLVTA KYQDLQENQR FVNVGLEKLN ESVLKVNELN KTLSKKSTEL TEKEKEARST LD KMLMEQN ESERKQEATE EIKKILKVQE EDIRKRKEVV MKSIQDIEPT ILEAQRGVKN IKKQQLTEIR SMVNPPSGVK IVM EAVCAI LGYQFSNWRD IQQFIRKDDF IHNIVHYDTT LHMKPQIRKY MEEEFLSDPN FTYETINRAS KACGPLYQWV NAQI NFSKV LENVDPLRQE MKRIEFESLK TKANLLAAEE MTQDLEASIE VSKQKYSLLI RDVEAIKTEM SNVQANLDRS ISLVK SLTF EKERWLNTTK QFSKTSQELI GNCIISSIYE TYFGHLNERE RGDMLVILKR LLGKFAVKYD VNYRFIDYLV TLDEKM KWL ECGLDKNDYF LENMSIVMNS QDAVPFLLDP SSHMITVISN YYGNKTVLLS FLEEGFVKRL ENAVRFGSVV IIQDGEF FD PIISRLISRE FNHAGNRVTV EIGDHEVDVS GDFKLFIHSC DPSGDIPIFL RSRVRLVHFV TNKESIETRI FDITLTEE N AEMQRKREDL IKLNTEYRLK LKNLEKRLLE ELNNSQGNML ENDELMVTLN NLKKEAMNIE KKLSESEEFF PQFDNLVEE YSIIGKHSVK IFSMLEKFGQ FHWFYGISIG QFLSCFKRVF IKKSRETRAA RTRVDEILWL LYQEVYCQFS TALDKKFKMI MAMTMFCLY KFDIESEQYK EAVLTMIGVL SESSDGVPKL TVDTNDDLRY LWDYVTTKSY ISALNWFKNE FFVDEWNIAD V VANSENNY FTMASERDVD GTFKLIELAK ASKESLKIIP LGSIENLNYA QEEISKSKIE GGWILLQNIQ MSLSWVKTYL HK HVEETKA AEEHEKFKMF MTCHLTGDKL PAPLLQRTDR VVYEDIPGIL DTVKDLWGSQ FFTGKISGVW SVYCTFLLSW FHA LITART RLVPHGFSKK YYFNDCDFQF ASVYLENVLA TNSTNNIPWA QVRDHIATIV YGGKIDEEKD LEVVAKLCAH VFCG SDNLQ IVPGVRIPQP LLQQSEEEER ARLTAILSNT IEPADSLSSW LQLPRESILD YERLQAKEVA SSTEQLLQEM UniProtKB: Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic |
-Macromolecule #2: Nuclear distribution protein PAC1
| Macromolecule | Name: Nuclear distribution protein PAC1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 57.030617 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
| Sequence | String: GMTNWQQQLP LTDTQKNELD KSVLRYLNWN YKQTVRHEHA QDYESVRHAI VTLSGFLLQE SVDRQEFISN NDTSNESMVD IDELLLPKK WNSIVRLQKK IIELEQNTET LVSQIKDLNT QVSELAQFKP TTSNGTSAHN VLKWIPRNLP SCLINVESSV T SVKLHPNL ...String: GMTNWQQQLP LTDTQKNELD KSVLRYLNWN YKQTVRHEHA QDYESVRHAI VTLSGFLLQE SVDRQEFISN NDTSNESMVD IDELLLPKK WNSIVRLQKK IIELEQNTET LVSQIKDLNT QVSELAQFKP TTSNGTSAHN VLKWIPRNLP SCLINVESSV T SVKLHPNL PIVFVATDHG KLYAFDLFNY TIPLASLQSH TKAITSMDVL FTNYTNSSKK NYLVIVTASK DLQIHVFKWV SE ECKFQQI RSLLGHEHIV SAVKIWQKNN DVHIASCSRD QTVKIWDFHN GWSLKTFQPH SQWVRSIDVL GDYIISGSHD TTL RLTHWP SGNGLSVGTG HEFPIEKVKF IHFIEDSPEI RFRTPSTDRY KNWGMQYCVS ASRDRTIKIW EIPLPTLMAH RAPI PNPTD SNFRCVLTLK GHLSWVRDIS IRGQYLFSCA DDKSVRCWDL NTGQCLHVWE KLHTGFVNCL DLDVDFDSNV TPRQM MVTG GLDCKSNVFM R UniProtKB: Nuclear distribution protein PAC1 |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information | 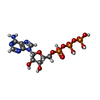 ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #4: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information | 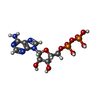 ChemComp-ADP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
| Details | streptavidin affinity grids were used |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.0 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 58.3 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z
Z Y
Y X
X