+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
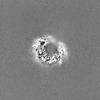
| Title | Human RAD52 open ring - ssDNA complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpen by DeepEMhancer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ssDNA binding protein /  DNA damage repair / Single-strand annealing / DNA damage repair / Single-strand annealing /  DNA BINDING PROTEIN DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdouble-strand break repair via single-strand annealing / DNA double-strand break processing involved in repair via single-strand annealing / DNA recombinase assembly /  mitotic recombination / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / mitotic recombination / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins /  protein-DNA complex / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination ...double-strand break repair via single-strand annealing / DNA double-strand break processing involved in repair via single-strand annealing / DNA recombinase assembly / protein-DNA complex / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination ...double-strand break repair via single-strand annealing / DNA double-strand break processing involved in repair via single-strand annealing / DNA recombinase assembly /  mitotic recombination / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / mitotic recombination / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins /  protein-DNA complex / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / double-strand break repair / protein-DNA complex / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / double-strand break repair /  single-stranded DNA binding / cellular response to oxidative stress / DNA recombination / protein-containing complex / single-stranded DNA binding / cellular response to oxidative stress / DNA recombination / protein-containing complex /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding /  nucleus nucleusSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.3 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.3 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Liang CC / West SC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, European Union, United Kingdom, European Union,  Switzerland, 8 items Switzerland, 8 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Mechanism of single-stranded DNA annealing by RAD52-RPA complex. Authors: Chih-Chao Liang / Luke A Greenhough / Laura Masino / Sarah Maslen / Ilirjana Bajrami / Marcel Tuppi / Mark Skehel / Ian A Taylor / Stephen C West /  Abstract: RAD52 is important for the repair of DNA double-stranded breaks, mitotic DNA synthesis and alternative telomere length maintenance. Central to these functions, RAD52 promotes the annealing of ...RAD52 is important for the repair of DNA double-stranded breaks, mitotic DNA synthesis and alternative telomere length maintenance. Central to these functions, RAD52 promotes the annealing of complementary single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and provides an alternative to BRCA2/RAD51-dependent homologous recombination repair. Inactivation of RAD52 in homologous-recombination-deficient BRCA1- or BRCA2-defective cells is synthetically lethal, and aberrant expression of RAD52 is associated with poor cancer prognosis. As a consequence, RAD52 is an attractive therapeutic target against homologous-recombination-deficient breast, ovarian and prostate cancers. Here we describe the structure of RAD52 and define the mechanism of annealing. As reported previously, RAD52 forms undecameric (11-subunit) ring structures, but these rings do not represent the active form of the enzyme. Instead, cryo-electron microscopy and biochemical analyses revealed that ssDNA annealing is driven by RAD52 open rings in association with replication protein-A (RPA). Atomic models of the RAD52-ssDNA complex show that ssDNA sits in a positively charged channel around the ring. Annealing is driven by the RAD52 N-terminal domains, whereas the C-terminal regions modulate the open-ring conformation and RPA interaction. RPA associates with RAD52 at the site of ring opening with critical interactions occurring between the RPA-interacting domain of RAD52 and the winged helix domain of RPA2. Our studies provide structural snapshots throughout the annealing process and define the molecular mechanism of ssDNA annealing by the RAD52-RPA complex. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_19253.map.gz emd_19253.map.gz | 156.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-19253-v30.xml emd-19253-v30.xml emd-19253.xml emd-19253.xml | 21.8 KB 21.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_19253_fsc.xml emd_19253_fsc.xml | 11.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_19253.png emd_19253.png | 112.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-19253.cif.gz emd-19253.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_19253_additional_1.map.gz emd_19253_additional_1.map.gz emd_19253_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19253_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19253_half_map_2.map.gz emd_19253_half_map_2.map.gz | 168.1 MB 165.1 MB 165.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19253 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19253 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19253 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19253 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 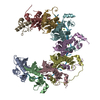 8rjwMC  8rilC  8rj3C  8rk2C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_19253.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_19253.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpen by DeepEMhancer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.85 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
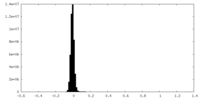
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Sharpen by -71.5 B Factor
| File | emd_19253_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpen by -71.5 B Factor | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
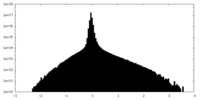
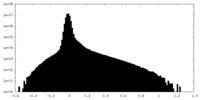
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_19253_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
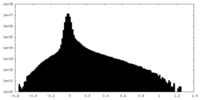
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_19253_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Open ring conformation of human RAD52 in complex with ssDNA
| Entire | Name: Open ring conformation of human RAD52 in complex with ssDNA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Open ring conformation of human RAD52 in complex with ssDNA
| Supramolecule | Name: Open ring conformation of human RAD52 in complex with ssDNA type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: Recombinant RAD52 purified from E. coli, and the open ring conformation was separated by cation exchange. The RAD52-ssDNA complex was reconstituted in vitro. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA repair protein RAD52 homolog
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA repair protein RAD52 homolog / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 9 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46.232656 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MSGTEEAILG GRDSHPAAGG GSVLCFGQCQ YTAEEYQAIQ KALRQRLGPE YISSRMAGGG QKVCYIEGHR VINLANEMFG YNGWAHSIT QQNVDFVDLN NGKFYVGVCA FVRVQLKDGS YHEDVGYGVS EGLKSKALSL EKARKEAVTD GLKRALRSFG N ALGNCILD ...String: MSGTEEAILG GRDSHPAAGG GSVLCFGQCQ YTAEEYQAIQ KALRQRLGPE YISSRMAGGG QKVCYIEGHR VINLANEMFG YNGWAHSIT QQNVDFVDLN NGKFYVGVCA FVRVQLKDGS YHEDVGYGVS EGLKSKALSL EKARKEAVTD GLKRALRSFG N ALGNCILD KDYLRSLNKL PRQLPLEVDL TKAKRQDLEP SVEEARYNSC RPNMALGHPQ LQQVTSPSRP SHAVIPADQD CS SRSLSSS AVESEATHQR KLRQKQLQQQ FRERMEKQQV RVSTPSAEKS EAAPPAPPVT HSTPVTVSEP LLEKDFLAGV TQE LIKTLE DNSEKWAVTP DAGDGVVKPS SRADPAQTSD TLALNNQMVT QNRTPHSVCH QKPQAKSGSW DLQTYSADQR TTGN WESHR KSQDMKKRKY DPS UniProtKB:  DNA repair protein RAD52 homolog DNA repair protein RAD52 homolog |
-Macromolecule #2: ssDNA
| Macromolecule | Name: ssDNA / type: dna / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 6.951477 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 39 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.15 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.25 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.75 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.25 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.75 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)