+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural mechanism for bidirectional actin cross-linking by T-plastin. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 119, Issue 37, Page e2205370119, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Sep 13, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Lin Mei / Matthew J Reynolds / Damien Garbett / Rui Gong / Tobias Meyer / Gregory M Alushin /  |
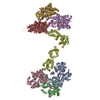
| PubMed Abstract | To orchestrate cell mechanics, trafficking, and motility, cytoskeletal filaments must assemble into higher-order networks whose local subcellular architecture and composition specify their functions. ...To orchestrate cell mechanics, trafficking, and motility, cytoskeletal filaments must assemble into higher-order networks whose local subcellular architecture and composition specify their functions. Cross-linking proteins bridge filaments at the nanoscale to control a network's μm-scale geometry, thereby conferring its mechanical properties and functional dynamics. While these interfilament linkages are key determinants of cytoskeletal function, their structural mechanisms remain poorly understood. Plastins/fimbrins are an evolutionarily ancient family of tandem calponin-homology domain (CHD) proteins required to construct multiple classes of actin networks, which feature diverse geometries specialized to power cytokinesis, microvilli and stereocilia biogenesis, and persistent cell migration. Here, we focus on the structural basis of actin network assembly by human T-plastin, a ubiquitously expressed isoform necessary for the maintenance of stable cellular protrusions generated by actin polymerization forces. By implementing a machine-learning-enabled cryo-electron microscopy pipeline for visualizing cross-linkers bridging multiple filaments, we uncover a sequential bundling mechanism enabling T-plastin to bridge pairs of actin filaments in both parallel and antiparallel orientations. T-plastin populates distinct structural landscapes in these two bridging orientations that are selectively compatible with actin networks featuring divergent architectures and functions. Our structural, biochemical, and cell biological data highlight inter-CHD linkers as key structural elements underlying flexible but stable cross-linking that are likely to be disrupted by T-plastin mutations that cause hereditary bone diseases. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:36067297 / PubMed:36067297 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (helical sym.) / EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.6 - 10.0 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-24323, PDB-7r94: EMDB-25494, PDB-7sx8: EMDB-25495, PDB-7sx9: EMDB-25496, PDB-7sxa: |
| Chemicals | 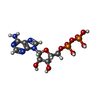 ChemComp-ADP: 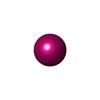 ChemComp-MG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / T-plastin / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / T-plastin /  plastin / plastin /  actin / actin /  filopodium / filopodium /  cytoskeleton / cell protrusion cytoskeleton / cell protrusion |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers