[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- SASDF65: Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8 homolog A (Ric8a) am... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDF65 |
|---|---|
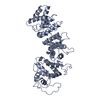
 Sample Sample | Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8 homolog A (Ric8a) amino acids 1-492
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationG-protein alpha-subunit binding / guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function |
| Biological species |   Bos taurus (cattle) Bos taurus (cattle) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2019Title: Structural underpinnings of Ric8A function as a G-protein α-subunit chaperone and guanine-nucleotide exchange factor. Authors: Dhiraj Srivastava / Lokesh Gakhar / Nikolai O Artemyev /  Abstract: Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8A (Ric8A) is an essential regulator of G protein α-subunits (Gα), acting as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor and a chaperone. We report two crystal ...Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8A (Ric8A) is an essential regulator of G protein α-subunits (Gα), acting as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor and a chaperone. We report two crystal structures of Ric8A, one in the apo form and the other in complex with a tagged C-terminal fragment of Gα. These structures reveal two principal domains of Ric8A: an armadillo-fold core and a flexible C-terminal tail. Additionally, they show that the Gα C-terminus binds to a highly-conserved patch on the concave surface of the Ric8A armadillo-domain, with selectivity determinants residing in the Gα sequence. Biochemical analysis shows that the Ric8A C-terminal tail is critical for its stability and function. A model of the Ric8A/Gα complex derived from crosslinking mass spectrometry and molecular dynamics simulations suggests that the Ric8A C-terminal tail helps organize the GTP-binding site of Gα. This study lays the groundwork for understanding Ric8A function at the molecular level. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Models
| Model #3128 |  Type: atomic / Comment: One state model / Chi-square value: 1.50747614912  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|---|
| Model #3129 |  Type: atomic / Comment: Fractional contribution in X-ray scattering: 59% / Chi-square value: 1.19852188057  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
| Model #3130 |  Type: atomic / Comment: Fractional contribution in X-ray scattering: 29% / Chi-square value: 1.19852188057  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
| Model #3131 |  Type: atomic / Comment: Fractional contribution in X-ray scattering: 12% / Chi-square value: 1.19852188057  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8 homolog A (Ric8a) amino acids 1-492 Specimen concentration: 10 mg/ml |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 20 mM Tris, 150 mM KCl, 5 % glycerol, 1 mM TCEP / pH: 8 |
| Entity #1575 | Name: Ric8a / Type: protein / Type: proteinDescription: Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8 homolog A Formula weight: 55.643 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Bos taurus / References: UniProt: Q5E9J8 Sequence: GHMADPRAVA DALETGEEDV VMEALRAYNR ENSQSFTFDD AQQEDRKRLA KLLVSVLEQG LPPSRRVIWL QSIRILSRDR SCLDSFTSRR SLQALACYAG ISASQGSVPE PLNMDVVLES LKCLCNLVLS SPVAQALAAE AGLVVRLAER VGLCRQSSFP HDVQFFDLRL ...Sequence: GHMADPRAVA DALETGEEDV VMEALRAYNR ENSQSFTFDD AQQEDRKRLA KLLVSVLEQG LPPSRRVIWL QSIRILSRDR SCLDSFTSRR SLQALACYAG ISASQGSVPE PLNMDVVLES LKCLCNLVLS SPVAQALAAE AGLVVRLAER VGLCRQSSFP HDVQFFDLRL LFLLTALRTD VRQQLFQELQ GVRLLTRALE LTLGMTEGER HPELLPPQET ERAMEILKVL FNITFDSIKR EVDEEDAALY RHLGTLLRHC VMLAAAGDRT EELHGHAVNL LGNLPVKCLD VLLTLEPHEG SLEFLGVNMD VIRVLLSFME KRLHQTHRLK ESVAPVLSVL TECARMHRPA RKFLKAQVLP PLRDVRTRPE VGELLRNKLV RLMTHLDTDV KRVAAEFLFV LCSESVPRFI KYTGYGNAAG LLAARGLMAG GRPEGQYSED EDTDTDEYKE AKASINPVTG RVEEKPPNPM EGMTEEQKEH EAMKLVNMFD KLSRH |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: Advanced Photon Source (APS), Argonne National Laboratory BioCAT 18ID City: Lemont, IL / 国: USA  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron Synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1033 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 3.5 mm Synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1033 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 3.5 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Pilatus3 X 1M / Pixsize x: 0.172 mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan | Measurement date: Oct 27, 2018 / Storage temperature: 4 °C / Cell temperature: 25 °C / Exposure time: 0.5 sec. / Unit: 1/A /
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

 SASDF65
SASDF65