[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
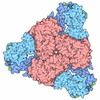
Yorodumi- PDB-8urw: Cyanobacterial RNA polymerase elongation complex with NusG and CTP -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8urw | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cyanobacterial RNA polymerase elongation complex with NusG and CTP | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  TRANSCRIPTION / TRANSCRIPTION /  Transcription regulation / Transcription regulation /  RNAP / NusG / RNAP / NusG /  cryo-EM cryo-EM | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtranscription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling /  DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription antitermination / DNA-templated transcription termination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription antitermination / DNA-templated transcription termination /  ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity /  DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase /  protein dimerization activity / DNA-templated transcription ...transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / protein dimerization activity / DNA-templated transcription ...transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling /  DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription antitermination / DNA-templated transcription termination / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription antitermination / DNA-templated transcription termination /  ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity /  DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase /  protein dimerization activity / DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / protein dimerization activity / DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding /  DNA binding / zinc ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.79 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.79 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Qayyum, M.Z. / Imashimizu, M. / Leanca, M. / Vishwakarma, R.K. / Bradley Riaz, A. / Yuzenkova, Y. / Murakami, K.S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2024Title: Structure and function of the Si3 insertion integrated into the trigger loop/helix of cyanobacterial RNA polymerase. Authors: M Zuhaib Qayyum / Masahiko Imashimizu / Miron Leanca / Rishi K Vishwakarma / Amber Riaz-Bradley / Yulia Yuzenkova / Katsuhiko S Murakami /    Abstract: Cyanobacteria and evolutionarily related chloroplasts of algae and plants possess unique RNA polymerases (RNAPs) with characteristics that distinguish them from canonical bacterial RNAPs. The largest ...Cyanobacteria and evolutionarily related chloroplasts of algae and plants possess unique RNA polymerases (RNAPs) with characteristics that distinguish them from canonical bacterial RNAPs. The largest subunit of cyanobacterial RNAP (cyRNAP) is divided into two polypeptides, β'1 and β'2, and contains the largest known lineage-specific insertion domain, Si3, located in the middle of the trigger loop and spanning approximately half of the β'2 subunit. In this study, we present the X-ray crystal structure of Si3 and the cryo-EM structures of the cyRNAP transcription elongation complex plus the NusG factor with and without incoming nucleoside triphosphate (iNTP) bound at the active site. Si3 has a well-ordered and elongated shape that exceeds the length of the main body of cyRNAP, fits into cavities of cyRNAP in the absence of iNTP bound at the active site and shields the binding site of secondary channel-binding proteins such as Gre and DksA. A small transition from the trigger loop to the trigger helix upon iNTP binding results in a large swing motion of Si3; however, this transition does not affect the catalytic activity of cyRNAP due to its minimal contact with cyRNAP, NusG, or DNA. This study provides a structural framework for understanding the evolutionary significance of these features unique to cyRNAP and chloroplast RNAP and may provide insights into the molecular mechanism of transcription in specific environment of photosynthetic organisms and organelle. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8urw.cif.gz 8urw.cif.gz | 829.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8urw.ent.gz pdb8urw.ent.gz | 604.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8urw.json.gz 8urw.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ur/8urw https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ur/8urw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ur/8urw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ur/8urw | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  42502MC  8embC  8syiC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 5 types, 6 molecules ABCDEZ
| #1: Protein |  Polymerase / RNAP subunit alpha / RNA polymerase subunit alpha / Transcriptase subunit alpha Polymerase / RNAP subunit alpha / RNA polymerase subunit alpha / Transcriptase subunit alphaMass: 33814.891 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoA, Synpcc7942_2209 / Production host: Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoA, Synpcc7942_2209 / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31L30, Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31L30,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase#2: Protein | |  Polymerase / RNAP subunit beta / RNA polymerase subunit beta / Transcriptase subunit beta Polymerase / RNAP subunit beta / RNA polymerase subunit beta / Transcriptase subunit betaMass: 123428.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoB, Synpcc7942_1522 / Production host: Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoB, Synpcc7942_1522 / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31N17, Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31N17,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase#3: Protein | |  Polymerase / RNAP subunit gamma / RNA polymerase subunit gamma / Transcriptase subunit gamma Polymerase / RNAP subunit gamma / RNA polymerase subunit gamma / Transcriptase subunit gammaMass: 71054.367 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoC1, Synpcc7942_1523 / Production host: Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoC1, Synpcc7942_1523 / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P42079, Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: P42079,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase#4: Protein | |  Polymerase / RNAP omega subunit / RNA polymerase omega subunit / Transcriptase subunit omega Polymerase / RNAP omega subunit / RNA polymerase omega subunit / Transcriptase subunit omegaMass: 8787.966 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoZ, Synpcc7942_1710 / Production host: Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoZ, Synpcc7942_1710 / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31MH9, Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31MH9,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase#5: Protein | |  Polymerase / RNAP subunit beta' / RNA polymerase subunit beta' / Transcriptase subunit beta' Polymerase / RNAP subunit beta' / RNA polymerase subunit beta' / Transcriptase subunit beta'Mass: 144006.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoC2, Synpcc7942_1524 / Production host: Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: rpoC2, Synpcc7942_1524 / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31N15, Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31N15,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules NT
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 12380.916 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 12251.828 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Protein / RNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules GR
| #6: Protein | Mass: 23117.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: nusG, Synpcc7942_0635 / Production host: Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) / Gene: nusG, Synpcc7942_0635 / Production host:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31QK2 Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q31QK2 |
|---|---|
| #9: RNA chain | Mass: 6863.198 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 4 molecules 



| #10: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #11: Chemical | | #12: Chemical | ChemComp-CTP / |  Cytidine triphosphate Cytidine triphosphate |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cyanobacterial RNA polymerase elongation complex with NusG and CTP Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#9 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: 40mM Tris-HCl 200mM KCl 1mM EDTA 1mM DTT 5mM MgCl2 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: OTHER / Nominal defocus max: 1750 nm / Nominal defocus min: 750 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY |
|---|---|
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.79 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 132172 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj