+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8kg6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
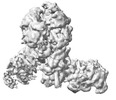
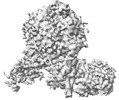
| Title | Yeast replisome in state I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  REPLICATION / REPLICATION /  replisome / replisome /  complex / complex /  DNA replication DNA replication | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information establishment of sister chromatid cohesion / DNA-templated DNA replication maintenance of fidelity / establishment of sister chromatid cohesion / DNA-templated DNA replication maintenance of fidelity /  gene conversion / maintenance of DNA repeat elements / Unwinding of DNA / replication fork arrest / DNA replication initiation / Cul8-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / meiotic chromosome segregation / epsilon DNA polymerase complex ... gene conversion / maintenance of DNA repeat elements / Unwinding of DNA / replication fork arrest / DNA replication initiation / Cul8-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / meiotic chromosome segregation / epsilon DNA polymerase complex ... establishment of sister chromatid cohesion / DNA-templated DNA replication maintenance of fidelity / establishment of sister chromatid cohesion / DNA-templated DNA replication maintenance of fidelity /  gene conversion / maintenance of DNA repeat elements / Unwinding of DNA / replication fork arrest / DNA replication initiation / Cul8-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / meiotic chromosome segregation / epsilon DNA polymerase complex / DNA strand elongation involved in mitotic DNA replication / MCM core complex / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / nuclear DNA replication / MCM complex binding / GINS complex / mitotic DNA replication preinitiation complex assembly / premeiotic DNA replication / pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling / gene conversion / maintenance of DNA repeat elements / Unwinding of DNA / replication fork arrest / DNA replication initiation / Cul8-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / meiotic chromosome segregation / epsilon DNA polymerase complex / DNA strand elongation involved in mitotic DNA replication / MCM core complex / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / nuclear DNA replication / MCM complex binding / GINS complex / mitotic DNA replication preinitiation complex assembly / premeiotic DNA replication / pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling /  SUMO binding / mitotic DNA replication / DNA replication proofreading / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / CMG complex / single-stranded DNA 3'-5' DNA exonuclease activity / establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / DNA replication checkpoint signaling / nuclear pre-replicative complex / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / MCM complex / DNA replication preinitiation complex / double-strand break repair via break-induced replication / mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling / replication fork protection complex / mitotic DNA replication initiation / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling / SUMO binding / mitotic DNA replication / DNA replication proofreading / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / CMG complex / single-stranded DNA 3'-5' DNA exonuclease activity / establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / DNA replication checkpoint signaling / nuclear pre-replicative complex / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / MCM complex / DNA replication preinitiation complex / double-strand break repair via break-induced replication / mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling / replication fork protection complex / mitotic DNA replication initiation / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling /  Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds; Exodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / leading strand elongation / nuclear chromosome / DNA unwinding involved in DNA replication / replication fork processing / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds; Exodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / leading strand elongation / nuclear chromosome / DNA unwinding involved in DNA replication / replication fork processing /  DNA replication origin binding / nuclear replication fork / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / DNA replication initiation / error-prone translesion synthesis / heterochromatin formation / DNA replication origin binding / nuclear replication fork / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / DNA replication initiation / error-prone translesion synthesis / heterochromatin formation /  base-excision repair, gap-filling / base-excision repair, gap-filling /  DNA helicase activity / meiotic cell cycle / DNA helicase activity / meiotic cell cycle /  replication fork / replication fork /  helicase activity / helicase activity /  base-excision repair / DNA-templated DNA replication / base-excision repair / DNA-templated DNA replication /  nucleosome assembly / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / double-strand break repair / nucleosome assembly / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / double-strand break repair /  single-stranded DNA binding / mitotic cell cycle / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / single-stranded DNA binding / mitotic cell cycle / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding /  double-stranded DNA binding / double-stranded DNA binding /  DNA helicase / DNA helicase /  DNA replication / DNA replication /  chromosome, telomeric region / chromosome, telomeric region /  DNA-directed DNA polymerase / DNA-directed DNA polymerase /  DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity /  cell cycle / cell cycle /  nucleotide binding / nucleotide binding /  mRNA binding / mRNA binding /  DNA repair / DNA damage response / DNA repair / DNA damage response /  chromatin binding / chromatin binding /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  DNA binding / zinc ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  nucleus / nucleus /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast)  Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.07 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.07 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dang, S. / Zhai, Y. / Feng, J. / Yu, D. / Xu, Z. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Hong Kong, 8items Hong Kong, 8items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Synergism between CMG helicase and leading strand DNA polymerase at replication fork. Authors: Zhichun Xu / Jianrong Feng / Daqi Yu / Yunjing Huo / Xiaohui Ma / Wai Hei Lam / Zheng Liu / Xiang David Li / Toyotaka Ishibashi / Shangyu Dang / Yuanliang Zhai /  Abstract: The replisome that replicates the eukaryotic genome consists of at least three engines: the Cdc45-MCM-GINS (CMG) helicase that separates duplex DNA at the replication fork and two DNA polymerases, ...The replisome that replicates the eukaryotic genome consists of at least three engines: the Cdc45-MCM-GINS (CMG) helicase that separates duplex DNA at the replication fork and two DNA polymerases, one on each strand, that replicate the unwound DNA. Here, we determined a series of cryo-electron microscopy structures of a yeast replisome comprising CMG, leading-strand polymerase Polε and three accessory factors on a forked DNA. In these structures, Polε engages or disengages with the motor domains of the CMG by occupying two alternative positions, which closely correlate with the rotational movement of the single-stranded DNA around the MCM pore. During this process, the polymerase remains stably coupled to the helicase using Psf1 as a hinge. This synergism is modulated by a concerted rearrangement of ATPase sites to drive DNA translocation. The Polε-MCM coupling is not only required for CMG formation to initiate DNA replication but also facilitates the leading-strand DNA synthesis mediated by Polε. Our study elucidates a mechanism intrinsic to the replisome that coordinates the activities of CMG and Polε to negotiate any roadblocks, DNA damage, and epigenetic marks encountered during translocation along replication forks. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8kg6.cif.gz 8kg6.cif.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8kg6.ent.gz pdb8kg6.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8kg6.json.gz 8kg6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kg/8kg6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kg/8kg6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kg/8kg6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kg/8kg6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  37211MC  8kg8C  8kg9C  8w7mC  8w7sC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA replication licensing factor ... , 5 types, 5 molecules 23467
| #1: Protein | Mass: 98911.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM2 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM2 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P29469, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P29469,  DNA helicase DNA helicase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 107653.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM3 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM3 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P24279 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P24279 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 105138.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM4 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM4 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P30665, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P30665,  DNA helicase DNA helicase |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 113110.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM6 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM6 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P53091, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P53091,  DNA helicase DNA helicase |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 95049.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM7 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM7 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P38132, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P38132,  DNA helicase DNA helicase |
-Protein , 5 types, 7 molecules 5EFGHKL
| #4: Protein |  Mass: 86505.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM5 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MCM5 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P29496 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P29496 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #11: Protein | Mass: 74324.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: CDC45 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: CDC45 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q08032 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q08032 | ||||
| #12: Protein | Mass: 104543.391 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: CTF4 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: CTF4 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q01454 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q01454#15: Protein | | Mass: 141296.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: TOF1 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: TOF1 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P53840 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P53840#16: Protein | |  Mass: 36402.590 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: CSM3 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: CSM3 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q04659 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q04659 |
-DNA replication complex GINS protein ... , 4 types, 4 molecules ABCD
| #7: Protein | Mass: 24230.576 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: PSF1 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: PSF1 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q12488 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q12488 |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein | Mass: 25096.807 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: PSF2 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: PSF2 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P40359 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P40359 |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 21977.135 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: PSF3 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: PSF3 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q12146 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q12146 |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 33983.617 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: SLD5 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: SLD5 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q03406 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: Q03406 |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #13: DNA chain | Mass: 22138.150 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
|---|---|
| #14: DNA chain | Mass: 18524.887 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) |
-DNA polymerase epsilon ... , 2 types, 2 molecules MN
| #17: Protein | Mass: 255992.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: POL2 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: POL2 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P21951 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P21951 |
|---|---|
| #18: Protein |  Mass: 78425.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: DPB2 / Production host: Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C (yeast) / Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: DPB2 / Production host:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P24482 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) / References: UniProt: P24482 |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 17 molecules 



| #19: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #20: Chemical |  Adenosine diphosphate Adenosine diphosphate#21: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #22: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: replisome complex in state I / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#18 / Source: RECOMBINANT / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#18 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.70 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K Details: blot with filter paper for 3-4 seconds before plunging. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 4.5 sec. / Electron dose: 53 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 4 / Num. of real images: 21776 Details: Images were collected in movie-mode containing 40 frames. |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV : GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm / Width: 5760 / Height: 4092 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.07 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 384519 / Algorithm: EXACT BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6XKL Accession code: 6XKL / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj













































