[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7uja: Cryo-EM structure of Human respiratory syncytial virus F variant ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7uja | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Human respiratory syncytial virus F variant (construct pXCS847A) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  VIRAL PROTEIN / RSV / RSVF / pre-fusion VIRAL PROTEIN / RSV / RSVF / pre-fusion | ||||||
| Function / homology | Precursor fusion glycoprotein F0, Paramyxoviridae / Fusion glycoprotein F0 / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane /  plasma membrane / Fusion glycoprotein F0 plasma membrane / Fusion glycoprotein F0 Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |   Respiratory syncytial virus Respiratory syncytial virus  Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lees, J.A. / Ammirati, M. / Han, S. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Transl Med / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Transl Med / Year: 2023Title: Rational design of a highly immunogenic prefusion-stabilized F glycoprotein antigen for a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Authors: Ye Che / Alexey V Gribenko / Xi Song / Luke D Handke / Kari S Efferen / Kristin Tompkins / Srinivas Kodali / Lorna Nunez / A Krishna Prasad / Lynn M Phelan / Mark Ammirati / Xiaodi Yu / ...Authors: Ye Che / Alexey V Gribenko / Xi Song / Luke D Handke / Kari S Efferen / Kristin Tompkins / Srinivas Kodali / Lorna Nunez / A Krishna Prasad / Lynn M Phelan / Mark Ammirati / Xiaodi Yu / Joshua A Lees / Wei Chen / Lyndsey Martinez / Vidia Roopchand / Seungil Han / Xiayang Qiu / John P DeVincenzo / Kathrin U Jansen / Philip R Dormitzer / Kena A Swanson /  Abstract: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the leading, global cause of serious respiratory disease in infants and is an important cause of respiratory illness in older adults. No RSV vaccine is currently ...Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the leading, global cause of serious respiratory disease in infants and is an important cause of respiratory illness in older adults. No RSV vaccine is currently available. The RSV fusion (F) glycoprotein is a key antigen for vaccine development, and its prefusion conformation is the target of the most potent neutralizing antibodies. Here, we describe a computational and experimental strategy for designing immunogens that enhance the conformational stability and immunogenicity of RSV prefusion F. We obtained an optimized vaccine antigen after screening nearly 400 engineered F constructs. Through in vitro and in vivo characterization studies, we identified F constructs that are more stable in the prefusion conformation and elicit ~10-fold higher serum-neutralizing titers in cotton rats than DS-Cav1. The stabilizing mutations of the lead construct (847) were introduced onto F glycoprotein backbones of strains representing the dominant circulating genotypes of the two major RSV subgroups, A and B. Immunization of cotton rats with a bivalent vaccine formulation of these antigens conferred complete protection against RSV challenge, with no evidence of disease enhancement. The resulting bivalent RSV prefusion F investigational vaccine has recently been shown to be efficacious against RSV disease in two pivotal phase 3 efficacy trials, one for passive protection of infants by immunization of pregnant women and the second for active protection of older adults by direct immunization. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7uja.cif.gz 7uja.cif.gz | 478.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7uja.ent.gz pdb7uja.ent.gz | 383.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7uja.json.gz 7uja.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uj/7uja https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uj/7uja ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uj/7uja ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uj/7uja | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  26562MC  7uj3C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RSV variant (construct pXCS847A) ... , 2 types, 6 molecules ACKPQR
| #1: Protein | Mass: 45025.391 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Mutation: I145S, S187I, D483S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Respiratory syncytial virus / Production host: Respiratory syncytial virus / Production host:  Mammalia (mammals) / References: UniProt: A0A7D5GVC1 Mammalia (mammals) / References: UniProt: A0A7D5GVC1#6: Protein | Mass: 12109.954 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Mutation: A100C Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Respiratory syncytial virus / Production host: Respiratory syncytial virus / Production host:  Mammalia (mammals) / References: UniProt: A0A7D5GVC1 Mammalia (mammals) / References: UniProt: A0A7D5GVC1 |
|---|
-Antibody , 4 types, 12 molecules BGLDHMEINFJO
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 26231.088 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host: Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host:  Mammalia (mammals) Mammalia (mammals)#3: Antibody | Mass: 23972.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host: Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host:  Mammalia (mammals) Mammalia (mammals)#4: Antibody | Mass: 25989.154 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host: Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host:  Mammalia (mammals) Mammalia (mammals)#5: Antibody | Mass: 23273.938 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host: Mus musculus (house mouse) / Production host:  Mammalia (mammals) Mammalia (mammals) |
|---|
-Sugars , 1 types, 3 molecules 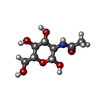
| #7: Sugar |  N-Acetylglucosamine N-Acetylglucosamine |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human respiratory syncytial virus F variant (construct pXCS847A) with Fabs AM14 and AM22 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Respiratory syncytial virus Respiratory syncytial virus | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 20 sec. / Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20_4459: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 420325 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C3 (3 fold cyclic : C3 (3 fold cyclic ) ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 183713 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj




