[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-4171: Dynein light intermediate chain region of the dynein tail/dynacti... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4171 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
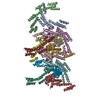
| Title | Dynein light intermediate chain region of the dynein tail/dynactin/BICDR1 complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Map of C terminal half of dynein tail in complex with dynactin and BICDR1, focussed on light intermediate chain. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  Cryo-EM / Cryo-EM /  Complex / Complex /  MOTOR PROTEIN MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdynein heavy chain binding / positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / establishment of spindle localization / positive regulation of spindle assembly /  P-body assembly / P-body assembly /  dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  cytoplasmic dynein complex ...dynein heavy chain binding / positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / establishment of spindle localization / positive regulation of spindle assembly / cytoplasmic dynein complex ...dynein heavy chain binding / positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / establishment of spindle localization / positive regulation of spindle assembly /  P-body assembly / P-body assembly /  dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein complex / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity /  cytoplasmic dynein complex / retrograde axonal transport / dynein light intermediate chain binding / nuclear migration / centrosome localization / dynein intermediate chain binding / microtubule-based movement / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / cytoplasmic microtubule / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / cytoplasmic dynein complex / retrograde axonal transport / dynein light intermediate chain binding / nuclear migration / centrosome localization / dynein intermediate chain binding / microtubule-based movement / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / cytoplasmic microtubule / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / cytoplasmic microtubule organization /  stress granule assembly / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / axon cytoplasm / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / MHC class II antigen presentation / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / mitotic spindle organization / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / stress granule assembly / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / axon cytoplasm / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / MHC class II antigen presentation / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / mitotic spindle organization / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus /  filopodium / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / filopodium / RHO GTPases Activate Formins /  kinetochore / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Aggrephagy / HCMV Early Events / Separation of Sister Chromatids / azurophil granule lumen / kinetochore / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Aggrephagy / HCMV Early Events / Separation of Sister Chromatids / azurophil granule lumen /  Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / late endosome / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / late endosome / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis /  cell cortex / cell cortex /  microtubule / microtubule /  cell division / cell division /  centrosome / Neutrophil degranulation / centrosome / Neutrophil degranulation /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / identical protein binding /  cytosol cytosolSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Urnavicius L / Lau CK | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2018 Journal: Nature / Year: 2018Title: Cryo-EM shows how dynactin recruits two dyneins for faster movement. Authors: Linas Urnavicius / Clinton K Lau / Mohamed M Elshenawy / Edgar Morales-Rios / Carina Motz / Ahmet Yildiz / Andrew P Carter /    Abstract: Dynein and its cofactor dynactin form a highly processive microtubule motor in the presence of an activating adaptor, such as BICD2. Different adaptors link dynein and dynactin to distinct cargoes. ...Dynein and its cofactor dynactin form a highly processive microtubule motor in the presence of an activating adaptor, such as BICD2. Different adaptors link dynein and dynactin to distinct cargoes. Here we use electron microscopy and single-molecule studies to show that adaptors can recruit a second dynein to dynactin. Whereas BICD2 is biased towards recruiting a single dynein, the adaptors BICDR1 and HOOK3 predominantly recruit two dyneins. We find that the shift towards a double dynein complex increases both the force and speed of the microtubule motor. Our 3.5 Å resolution cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of a dynein tail-dynactin-BICDR1 complex reveals how dynactin can act as a scaffold to coordinate two dyneins side-by-side. Our work provides a structural basis for understanding how diverse adaptors recruit different numbers of dyneins and regulate the motile properties of the dynein-dynactin transport machine. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4171.map.gz emd_4171.map.gz | 287.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4171-v30.xml emd-4171-v30.xml emd-4171.xml emd-4171.xml | 14.3 KB 14.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_4171.png emd_4171.png | 111.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-4171.cif.gz emd-4171.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4171 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4171 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4171 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4171 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6f1yMC  4168C  4169C 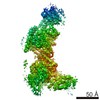 4170C  4172C  4177C  5owoC  6f1tC  6f1uC  6f1vC  6f1zC  6f38C  6f3aC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4171.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4171.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 824 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map of C terminal half of dynein tail in complex with dynactin and BICDR1, focussed on light intermediate chain. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.34 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1
| Entire | Name: Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1
| Supramolecule | Name: Two dynein tail domains bound to dynactin and BICDR1 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1,Dynein heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1,Dynein heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.117113 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) |
| Sequence | String: SLIESVRTYE RTCEKVEERN TISLLVAGLK KEVQALIAEG IALVWESYKL DPYVQRLAET VFNFQEKVDD LLIIEEKIDL EVRSLETCM YDHKTFSEIL NRVQKAVDDL NLHSYSNLPI WVNKLDMEIE RILGVRLQAG LRAWTQVLL(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) ...String: SLIESVRTYE RTCEKVEERN TISLLVAGLK KEVQALIAEG IALVWESYKL DPYVQRLAET VFNFQEKVDD LLIIEEKIDL EVRSLETCM YDHKTFSEIL NRVQKAVDDL NLHSYSNLPI WVNKLDMEIE RILGVRLQAG LRAWTQVLL(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)LEESY SAVMGIVSEV EQYVKV (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK)(UNK) (UNK)(UNK) UniProtKB: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 light intermediate chain 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 light intermediate chain 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 38.502941 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) |
| Sequence | String: SSILSEVSTR ARSKLPSGKN ILVFGEDGSG KTTLMTKLQG AEHGKKGRGL EYLYLSVHDE DRDDHTRCNV WILDGDLYHK GLLKFAVSA ESLPETLVIF VADMSRPWTV MESLQKWASV LREHIDKMKI PPEKMRELER KFVKDFQDYM EPEEGCQGSP Q RRGPLTSG ...String: SSILSEVSTR ARSKLPSGKN ILVFGEDGSG KTTLMTKLQG AEHGKKGRGL EYLYLSVHDE DRDDHTRCNV WILDGDLYHK GLLKFAVSA ESLPETLVIF VADMSRPWTV MESLQKWASV LREHIDKMKI PPEKMRELER KFVKDFQDYM EPEEGCQGSP Q RRGPLTSG SDEENVALPL GDNVLTHNLG IPVLVVCTKC DAVSVLEKEH DYRDEHLDFI QSHLRRFCLQ YGAALIYTSV KE EKNLDLL YKYIVHKTYG FHFTTPALVV EKDAVFIPAG WDNEKKIAIL HENFTTVKPE DAYEDFIVKP PVRKLVHDKE LAA EDEQVF LMKQQSLLAK Q UniProtKB: Cytoplasmic dynein 1 light intermediate chain 2 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy Bright-field microscopy |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 52.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: Details: Initial model low pass filtered to 50 A |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: RELION |
| Final 3D classification | Software - Name: RELION Details: 3D classification focussed on light intermediate chain region without alignments |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: RELION Details: Particle signal subtraction used to remove parts of the complex outside of the C terminal half of dynein tail domains. |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: RELION / Number images used: 113987 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6f1y: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller