+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of full-length LexA bound to a RecA filament | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened map used for model building and refinement | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Damage response /  signal transduction / signal transduction /  SIGNALING PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN /  SIGNALING PROTEIN-DNA complex SIGNALING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information repressor LexA / repressor LexA /  DNA polymerase V complex / DNA polymerase V complex /  homologous recombination / homologous recombination /  recombinational repair / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity / response to ionizing radiation / recombinational repair / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity / response to ionizing radiation /  SOS response / SOS response /  translesion synthesis / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA ... translesion synthesis / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA ... repressor LexA / repressor LexA /  DNA polymerase V complex / DNA polymerase V complex /  homologous recombination / homologous recombination /  recombinational repair / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity / response to ionizing radiation / recombinational repair / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity / response to ionizing radiation /  SOS response / SOS response /  translesion synthesis / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / translesion synthesis / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA /  cell motility / cell motility /  protein-DNA complex / protein-DNA complex /  single-stranded DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / DNA recombination / single-stranded DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / DNA recombination /  DNA replication / damaged DNA binding / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / serine-type endopeptidase activity / DNA replication / damaged DNA binding / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / serine-type endopeptidase activity /  DNA repair / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA-templated transcription / DNA damage response / DNA repair / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA-templated transcription / DNA damage response /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  proteolysis / proteolysis /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.93 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.93 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cory MB / Li A / Kohli RM | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: The LexA-RecA* structure reveals a cryptic lock-and-key mechanism for SOS activation. Authors: Michael B Cory / Allen Li / Christina M Hurley / Peter J Carman / Ruth A Pumroy / Zachary M Hostetler / Ryann M Perez / Yarra Venkatesh / Xinning Li / Kushol Gupta / E James Petersson / Rahul M Kohli /  Abstract: The bacterial SOS response plays a key role in adaptation to DNA damage, including genomic stress caused by antibiotics. SOS induction begins when activated RecA*, an oligomeric nucleoprotein ...The bacterial SOS response plays a key role in adaptation to DNA damage, including genomic stress caused by antibiotics. SOS induction begins when activated RecA*, an oligomeric nucleoprotein filament that forms on single-stranded DNA, binds to and stimulates autoproteolysis of the repressor LexA. Here, we present the structure of the complete Escherichia coli SOS signal complex, constituting full-length LexA bound to RecA*. We uncover an extensive interface unexpectedly including the LexA DNA-binding domain, providing a new molecular rationale for ordered SOS gene induction. We further find that the interface involves three RecA subunits, with a single residue in the central engaged subunit acting as a molecular key, inserting into an allosteric binding pocket to induce LexA cleavage. Given the pro-mutagenic nature of SOS activation, our structural and mechanistic insights provide a foundation for developing new therapeutics to slow the evolution of antibiotic resistance. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_41579.map.gz emd_41579.map.gz | 57.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-41579-v30.xml emd-41579-v30.xml emd-41579.xml emd-41579.xml | 25.4 KB 25.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_41579_fsc.xml emd_41579_fsc.xml emd_41579_fsc_2.xml emd_41579_fsc_2.xml | 8.4 KB 8.4 KB | Display Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_41579.png emd_41579.png | 84.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-41579.cif.gz emd-41579.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_41579_additional_1.map.gz emd_41579_additional_1.map.gz emd_41579_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41579_half_map_1.map.gz emd_41579_half_map_2.map.gz emd_41579_half_map_2.map.gz | 32.5 MB 59.3 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41579 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41579 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41579 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-41579 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8trgMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_41579.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_41579.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened map used for model building and refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.38 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Unsharpened final map from data processing
| File | emd_41579_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened final map from data processing | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map of final map
| File | emd_41579_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map of final map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map of final map
| File | emd_41579_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map of final map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : SOS Signal Complex consisting of RecA, ssDNA, and LexA
| Entire | Name: SOS Signal Complex consisting of RecA, ssDNA, and LexA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: SOS Signal Complex consisting of RecA, ssDNA, and LexA
| Supramolecule | Name: SOS Signal Complex consisting of RecA, ssDNA, and LexA type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: K12 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: K12 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 480 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: RecA* activated filament
| Supramolecule | Name: RecA* activated filament / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1, #3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: K12 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: K12 |
-Supramolecule #3: LexA Dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: LexA Dimer / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: K12 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain: K12 |
-Macromolecule #1: Protein RecA
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein RecA / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.119551 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MGSSHHHHHH HHHHHHSSGE NLYFQGMAID ENKQKALAAA LGQIEKQFGK GSIMRLGEDR SMDVETISTG SLSLDIALGA GGLPMGRIV EIYGPESSGK TTLTLQVIAA AQREGKTCAF IDAEHALDPI YARKLGVDID NLLCSQPDTG EQALEICDAL A RSGAVDVI ...String: MGSSHHHHHH HHHHHHSSGE NLYFQGMAID ENKQKALAAA LGQIEKQFGK GSIMRLGEDR SMDVETISTG SLSLDIALGA GGLPMGRIV EIYGPESSGK TTLTLQVIAA AQREGKTCAF IDAEHALDPI YARKLGVDID NLLCSQPDTG EQALEICDAL A RSGAVDVI VVDSVAALTP KAEIEGEIGD SHMGLAARMM SQAMRKLAGN LKQSNTLLIF INQIRMKIGV MFGNPETTTG GN ALKFYAS VRLDIRRIGA VKEGENVVGS ETRVKVVKNK IAAPFKQAEF QILYGEGINF YGELVDLGVK EKLIEKAGAW YSY KGEKIG QGKANATAWL KDNPETAKEI EKKVRELLLS NPNSTPDFSV DDSEGVAETN EDF UniProtKB: Protein RecA |
-Macromolecule #2: LexA repressor
| Macromolecule | Name: LexA repressor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.612887 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) (bacteria) |
| Sequence | String: GSHMKALTAR QQEVFDLIRD HISQTGMPPT RAEIAQRLGF RSPNAAEEHL KALARKGVIE IVSGASRGIR LLQEEEEGLP LVGRVAAGE PLLAQQHIEG HYQVDPSLFK PNADFLLRVS GMSMKDIGIM DGDLLAVHKT QDVRNGQVVV ARIDDEVTVA R LKKQGNKV ...String: GSHMKALTAR QQEVFDLIRD HISQTGMPPT RAEIAQRLGF RSPNAAEEHL KALARKGVIE IVSGASRGIR LLQEEEEGLP LVGRVAAGE PLLAQQHIEG HYQVDPSLFK PNADFLLRVS GMSMKDIGIM DGDLLAVHKT QDVRNGQVVV ARIDDEVTVA R LKKQGNKV ELLPENSEFK PIVVDLRQQS FTIEGLAVGV IRNGDWL UniProtKB:  LexA repressor LexA repressor |
-Macromolecule #3: DNA (27-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (27-MER) / type: dna / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8.618482 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG) |
-Macromolecule #4: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: AGS |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.247 Da |
| Chemical component information | 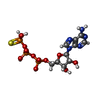 ChemComp-AGS: |
-Macromolecule #5: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.2 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: 70 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 2 mM TCEP, 0.25 mM ATPyS | ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 10 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.03 kPa / Details: 25 mA current | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: Blotting time of 7.0 s; 0.0 blot force. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 64000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 64000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Details | Preliminary grid screening was done manually |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 2748 / Average exposure time: 5.35 sec. / Average electron dose: 46.2 e/Å2 / Details: 40 frames collected per movie |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | Chain - Source name: AlphaFold / Chain - Initial model type: in silico model Details: The initial model was generated via benchling plugin for full-length construct sequence |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-8trg: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z
Z Y
Y X
X