+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | ion channel | |||||||||
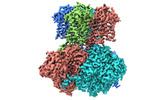
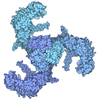
 Map data Map data | composite map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  ion channel / ion channel /  TRANSPORT PROTEIN TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintracellular sodium-activated potassium channel activity / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / potassium ion transmembrane transport /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jiang DH / Zhang JT | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis of human Slo2.2 channel gating and modulation. Authors: Jiangtao Zhang / Shiqi Liu / Junping Fan / Rui Yan / Bo Huang / Feng Zhou / Tian Yuan / Jianke Gong / Zhuo Huang / Daohua Jiang /  Abstract: The sodium-activated Slo2.2 channel is abundantly expressed in the brain, playing a critical role in regulating neuronal excitability. The Na-binding site and the underlying mechanisms of Na- ...The sodium-activated Slo2.2 channel is abundantly expressed in the brain, playing a critical role in regulating neuronal excitability. The Na-binding site and the underlying mechanisms of Na-dependent activation remain unclear. Here, we present cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of human Slo2.2 in closed, open, and inhibitor-bound form at resolutions of 2.6-3.2 Å, revealing gating mechanisms of Slo2.2 regulation by cations and a potent inhibitor. The cytoplasmic gating ring domain of the closed Slo2.2 harbors multiple K and Zn sites, which stabilize the channel in the closed conformation. The open Slo2.2 structure reveals at least two Na-sensitive sites where Na binding induces expansion and rotation of the gating ring that opens the inner gate. Furthermore, a potent inhibitor wedges into a pocket formed by pore helix and S6 helix and blocks the pore. Together, our results provide a comprehensive structural framework for the investigation of Slo2.2 channel gating, Na sensation, and inhibition. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_34858.map.gz emd_34858.map.gz | 59.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-34858-v30.xml emd-34858-v30.xml emd-34858.xml emd-34858.xml | 23.7 KB 23.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_34858.png emd_34858.png | 34.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_34858_additional_1.map.gz emd_34858_additional_1.map.gz emd_34858_additional_2.map.gz emd_34858_additional_2.map.gz emd_34858_additional_3.map.gz emd_34858_additional_3.map.gz emd_34858_additional_4.map.gz emd_34858_additional_4.map.gz emd_34858_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34858_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34858_half_map_2.map.gz emd_34858_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.3 MB 58.8 MB 59.3 MB 59.6 MB 59.3 MB 59.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34858 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34858 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34858 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34858 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8hkqMC  8hirC  8hk6C  8hkfC  8hkkC  8hkmC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_34858.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_34858.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | composite map | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: TMD half map A
| File | emd_34858_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | TMD half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: TMD map
| File | emd_34858_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | TMD map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: TMD half map B
| File | emd_34858_additional_3.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | TMD half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: gating ring map
| File | emd_34858_additional_4.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | gating ring map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: gating ring half map A
| File | emd_34858_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | gating ring half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: gating ring half map B
| File | emd_34858_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | gating ring half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ion channel
| Entire | Name: ion channel |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ion channel
| Supramolecule | Name: ion channel / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium channel subfamily T member 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium channel subfamily T member 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 139.865234 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MPLPDGARTP GGVCREARGG GYTNRTFEFD DGQCAPRRPC AGDGALLDTA GFKMSDLDSE VLPLPPRYRF RDLLLGDPSF QNDDRVQVE FYVNENTFKE RLKLFFIKNQ RSSLRIRLFN FSLKLLTCLL YIVRVLLDDP ALGIGCWGCP KQNYSFNDSS S EINWAPIL ...String: MPLPDGARTP GGVCREARGG GYTNRTFEFD DGQCAPRRPC AGDGALLDTA GFKMSDLDSE VLPLPPRYRF RDLLLGDPSF QNDDRVQVE FYVNENTFKE RLKLFFIKNQ RSSLRIRLFN FSLKLLTCLL YIVRVLLDDP ALGIGCWGCP KQNYSFNDSS S EINWAPIL WVERKMTLWA IQVIVAIISF LETMLLIYLS YKGNIWEQIF RVSFVLEMIN TLPFIITIFW PPLRNLFIPV FL NCWLAKH ALENMINDFH RAILRTQSAM FNQVLILFCT LLCLVFTGTC GIQHLERAGE NLSLLTSFYF CIVTFSTVGY GDV TPKIWP SQLLVVIMIC VALVVLPLQF EELVYLWMER QKSGGNYSRH RAQTEKHVVL CVSSLKIDLL MDFLNEFYAH PRLQ DYYVV ILCPTEMDVQ VRRVLQIPLW SQRVIYLQGS ALKDQDLMRA KMDNGEACFI LSSRNEVDRT AADHQTILRA WAVKD FAPN CPLYVQILKP ENKFHVKFAD HVVCEEECKY AMLALNCICP ATSTLITLLV HTSRGQEGQE SPEQWQRMYG RCSGNE VYH IRMGDSKFFR EYEGKSFTYA AFHAHKKYGV CLIGLKREDN KSILLNPGPR HILAASDTCF YINITKEENS AFIFKQE EK RKKRAFSGQG LHEGPARLPV HSIIASMGTV AMDLQGTEHR PTQSGGGGGG SKLALPTENG SGSRRPSIAP VLELADSS A LLPCDLLSDQ SEDEVTPSDD EGLSVVEYVK GYPPNSPYIG SSPTLCHLLP VKAPFCCLRL DKGCKHNSYE DAKAYGFKN KLIIVSAETA GNGLYNFIVP LRAYYRSRKE LNPIVLLLDN KPDHHFLEAI CCFPMVYYME GSVDNLDSLL QCGIIYADNL VVVDKESTM SAEEDYMADA KTIVNVQTMF RLFPSLSITT ELTHPSNMRF MQFRAKDSYS LALSKLEKRE RENGSNLAFM F RLPFAAGR VFSISMLDTL LYQSFVKDYM ITITRLLLGL DTTPGSGYLC AMKITEGDLW IRTYGRLFQK LCSSSAEIPI GI YRTESHV FSTSEPHDLR AQSQISVNVE DCEDTREVKG PWGSRAGTGG SSQGRHTGGG DPAEHPLLRR KSLQWARRLS RKA PKQAGR AAAAEWISQQ RLSLYRRSER QELSELVKNR MKHLGLPTTG YDEMNDHQNT LSYVLINPPP DTRLEPSDIV YLIR SDPLA HVASSSQSRK SSCSHKLSSC NPETRDETQL UniProtKB: Potassium channel subfamily T member 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: ~{N}-[(1~{S})-1-[3-(2-methoxypyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]e...
| Macromolecule | Name: ~{N}-[(1~{S})-1-[3-(2-methoxypyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]ethyl]-2-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazole-3-carboxamide type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: LQ9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 396.324 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-LQ9: |
-Macromolecule #3: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 11 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: SODIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: SODIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.99 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: RANDOM ASSIGNMENT |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 40913 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z
Z Y
Y X
X