[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-33285: Structure of human R-type voltage-gated CaV2.3-alpha2/delta1-beta... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human R-type voltage-gated CaV2.3-alpha2/delta1-beta1 channel complex in the ligand-free (apo) state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of muscle contraction / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential /  L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity ...positive regulation of muscle contraction / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity ...positive regulation of muscle contraction / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential /  L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / NCAM1 interactions / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / NCAM1 interactions / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel /  voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuromuscular junction development / neuronal dense core vesicle / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / regulation of calcium ion transport / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / neuromuscular junction development / neuronal dense core vesicle / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / regulation of calcium ion transport / calcium ion import across plasma membrane /  voltage-gated calcium channel activity / voltage-gated calcium channel activity /  sarcoplasmic reticulum / Regulation of insulin secretion / calcium ion transmembrane transport / cellular response to amyloid-beta / calcium ion transport / chemical synaptic transmission / neuronal cell body / sarcoplasmic reticulum / Regulation of insulin secretion / calcium ion transmembrane transport / cellular response to amyloid-beta / calcium ion transport / chemical synaptic transmission / neuronal cell body /  synapse / synapse /  calcium ion binding / extracellular exosome / calcium ion binding / extracellular exosome /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gao Y / Qiu Y / Wei Y / Dong Y / Zhang XC / Zhao Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Molecular insights into the gating mechanisms of voltage-gated calcium channel Ca2.3. Authors: Yiwei Gao / Shuai Xu / Xiaoli Cui / Hao Xu / Yunlong Qiu / Yiqing Wei / Yanli Dong / Boling Zhu / Chao Peng / Shiqi Liu / Xuejun Cai Zhang / Jianyuan Sun / Zhuo Huang / Yan Zhao /  Abstract: High-voltage-activated R-type Ca2.3 channel plays pivotal roles in many physiological activities and is implicated in epilepsy, convulsions, and other neurodevelopmental impairments. Here, we ...High-voltage-activated R-type Ca2.3 channel plays pivotal roles in many physiological activities and is implicated in epilepsy, convulsions, and other neurodevelopmental impairments. Here, we determine the high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of human Ca2.3 in complex with the α2δ1 and β1 subunits. The VSD is stabilized in the resting state. Electrophysiological experiments elucidate that the VSD is not required for channel activation, whereas the other VSDs are essential for channel opening. The intracellular gate is blocked by the W-helix. A pre-W-helix adjacent to the W-helix can significantly regulate closed-state inactivation (CSI) by modulating the association and dissociation of the W-helix with the gate. Electrostatic interactions formed between the negatively charged domain on S6, which is exclusively conserved in the Ca2 family, and nearby regions at the alpha-interacting domain (AID) and S4-S5 helix are identified. Further functional analyses indicate that these interactions are critical for the open-state inactivation (OSI) of Ca2 channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33285.map.gz emd_33285.map.gz | 118.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33285-v30.xml emd-33285-v30.xml emd-33285.xml emd-33285.xml | 25 KB 25 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33285.png emd_33285.png | 122.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33285_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33285_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33285_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33285_half_map_2.map.gz | 115.9 MB 115.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33285 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33285 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33285 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33285 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7xlqMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33285.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33285.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_33285_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_33285_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human R-type voltage-gated calcium channel CaV2.3-alpha2/delta1-b...
| Entire | Name: Human R-type voltage-gated calcium channel CaV2.3-alpha2/delta1-beta1 complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human R-type voltage-gated calcium channel CaV2.3-alpha2/delta1-b...
| Supramolecule | Name: Human R-type voltage-gated calcium channel CaV2.3-alpha2/delta1-beta1 complex type: complex / ID: 1 / Chimera: Yes / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1, #3, #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Voltage-dependent R-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1E
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent R-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1E type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 262.055984 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MARFGEAVVA RPGSGDGDSD QSRNRQGTPV PASGQAAAYK QTKAQRARTM ALYNPIPVRQ NCFTVNRSLF IFGEDNIVRK YAKKLIDWP PFEYMILATI IANCIVLALE QHLPEDDKTP MSRRLEKTEP YFIGIFCFEA GIKIVALGFI FHKGSYLRNG W NVMDFIVV ...String: MARFGEAVVA RPGSGDGDSD QSRNRQGTPV PASGQAAAYK QTKAQRARTM ALYNPIPVRQ NCFTVNRSLF IFGEDNIVRK YAKKLIDWP PFEYMILATI IANCIVLALE QHLPEDDKTP MSRRLEKTEP YFIGIFCFEA GIKIVALGFI FHKGSYLRNG W NVMDFIVV LSGILATAGT HFNTHVDLRT LRAVRVLRPL KLVSGIPSLQ IVLKSIMKAM VPLLQIGLLL FFAILMFAII GL EFYSGKL HRACFMNNSG ILEGFDPPHP CGVQGCPAGY ECKDWIGPND GITQFDNILF AVLTVFQCIT MEGWTTVLYN TND ALGATW NWLYFIPLII IGSFFVLNLV LGVLSGEFAK ERERVENRRA FMKLRRQQQI ERELNGYRAW IDKAEEVMLA EENK NAGTS ALEVLRRATI KRSRTEAMTR DSSDEHCVDI SSVGTPLARA SIKSAKVDGV SYFRHKERLL RISIRHMVKS QVFYW IVLS LVALNTACVA IVHHNQPQWL THLLYYAEFL FLGLFLLEMS LKMYGMGPRL YFHSSFNCFD FGVTVGSIFE VVWAIF RPG TSFGISVLRA LRLLRIFKIT KYWASLRNLV VSLMSSMKSI ISLLFLLFLF IVVFALLGMQ LFGGRFNFND GTPSANF DT FPAAIMTVFQ ILTGEDWNEV MYNGIRSQGG VSSGMWSAIY FIVLTLFGNY TLLNVFLAIA VDNLANAQEL TKDEQEEE E AFNQKHALQK AKEVSPMSAP NMPSIERDRR RRHHMSMWEP RSSHLRERRR RHHMSVWEQR TSQLRKHMQM SSQEALNRE EAPTMNPLNP LNPLSSLNPL NAHPSLYRRP RAIEGLALGL ALEKFEEERI SRGGSLKGDG GDRSSALDNQ RTPLSLGQRE PPWLARPCH GNCDPTQQEA GGGEAVVTFE DRARHRQSQR RSRHRRVRTE GKESSSASRS RSASQERSLD EAMPTEGEKD H ELRGNHGA KEPTIQEERA QDLRRTNSLM VSRGSGLAGG LDEADTPLVL PHPELEVGKH VVLTEQEPEG SSEQALLGNV QL DMGRVIS QSEPDLSCIT ANTDKATTES TSVTVAIPDV DPLVDSTVVH ISNKTDGEAS PLKEAEIRED EEEVEKKKQK KEK RETGKA MVPHSSMFIF STTNPIRRAC HYIVNLRYFE MCILLVIAAS SIALAAEDPV LTNSERNKVL RYFDYVFTGV FTFE MVIKM IDQGLILQDG SYFRDLWNIL DFVVVVGALV AFALANALGT NKGRDIKTIK SLRVLRVLRP LKTIKRLPKL KAVFD CVVT SLKNVFNILI VYKLFMFIFA VIAVQLFKGK FFYCTDSSKD TEKECIGNYV DHEKNKMEVK GREWKRHEFH YDNIIW ALL TLFTVSTGEG WPQVLQHSVD VTEEDRGPSR SNRMEMSIFY VVYFVVFPFF FVNIFVALII ITFQEQGDKM MEECSLE KN ERACIDFAIS AKPLTRYMPQ NRHTFQYRVW HFVVSPSFEY TIMAMIALNT VVLMMKYYSA PCTYELALKY LNIAFTMV F SLECVLKVIA FGFLNYFRDT WNIFDFITVI GSITEIILTD SKLVNTSGFN MSFLKLFRAA RLIKLLRQGY TIRILLWTF VQSFKALPYV CLLIAMLFFI YAIIGMQVFG NIKLDEESHI NRHNNFRSFF GSLMLLFRSA TGEAWQEIML SCLGEKGCEP DTTAPSGQN ENERCGTDLA YVYFVSFIFF CSFLMLNLFV AVIMDNFEYL TRDSSILGPH HLDEFVRVWA EYDRAACGRI H YTEMYEML TLMSPPLGLG KRCPSKVAYK RLVLMNMPVA EDMTVHFTST LMALIRTALD IKIAKGGADR QQLDSELQKE TL AIWPHLS QKMLDLLVPM PKASDLTVGK IYAAMMIMDY YKQSKVKKQR QQLEEQKNAP MFQRMEPSSL PQEIIANAKA LPY LQQDPV SGLSGRSGYP SMSPLSPQDI FQLACMDPAD DGQFQERQSL EPEVSELKSV QPSNHGIYLP SDTQEHAGSG RASS MPRLT VDPQVVTDPS SMRRSFSTIR DKRSNSSWLE EFSMERSSEN TYKSRRRSYH SSLRLSAHRL NSDSGHKSDT HRSGG RERG RSKERKHLLS PDVSRCNSEE RGTQADWESP ERRQSRSPSE GRSQTPNRQG TGSLSESSIP SVSDTSTPRR SRRQLP PVP PKPRPLLSYS SLIRHAGSIS PPADGSEEGS PLTSQALESN NACLTESSNS PHPQQSQHAS PQRYISEPYL ALHEDSH AS DCGEEETLTF EAAVATSLGR SNTIGSAPPL RHSWQMPNGH YRRRRRGGPG PGMMCGAVNN LLSDTEEDDK C |
-Macromolecule #2: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 122.034352 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: FPSAVTIKSW VDKMQEDLVT LAKTASGVNQ LVDIYEKYQD LYTVEPNNAR QLVEIAARDI EKLLSNRSKA LVRLALEAEK VQAAHQWRE DFASNEVVYY NAKDDLDPEK NDSEPGSQRI KPVFIEDANF GRQISYQHAA VHIPTDIYEG STIVLNELNW T SALDEVFK ...String: FPSAVTIKSW VDKMQEDLVT LAKTASGVNQ LVDIYEKYQD LYTVEPNNAR QLVEIAARDI EKLLSNRSKA LVRLALEAEK VQAAHQWRE DFASNEVVYY NAKDDLDPEK NDSEPGSQRI KPVFIEDANF GRQISYQHAA VHIPTDIYEG STIVLNELNW T SALDEVFK KNREEDPSLL WQVFGSATGL ARYYPASPWV DNSRTPNKID LYDVRRRPWY IQGAASPKDM LILVDVSGSV SG LTLKLIR TSVSEMLETL SDDDFVNVAS FNSNAQDVSC FQHLVQANVR NKKVLKDAVN NITAKGITDY KKGFSFAFEQ LLN YNVSRA NCNKIIMLFT DGGEERAQEI FNKYNKDKKV RVFTFSVGQH NYDRGPIQWM ACENKGYYYE IPSIGAIRIN TQEY LDVLG RPMVLAGDKA KQVQWTNVYL DALELGLVIT GTLPVFNITG QFENKTNLKN QLILGVMGVD VSLEDIKRLT PRFTL CPNG YYFAIDPNGY VLLHPNLQPK PIGVGIPTIN LRKRRPNIQN PKSQEPVTLD FLDAELENDI KVEIRNKMID GESGEK TFR TLVKSQDERY IDKGNRTYTW TPVNGTDYSL ALVLPTYSFY YIKAKLEETI TQARYSETLK PDNFEESGYT FIAPRDY CN DLKISDNNTE FLLNFNEFID RKTPNNPSCN ADLINRVLLD AGFTNELVQN YWSKQKNIKG VKARFVVTDG GITRVYPK E AGENWQENPE TYEDSFYKRS LDNDNYVFTA PYFNKSGPGA YESGIMVSKA VEIYIQGKLL KPAVVGIKID VNSWIENFT KTSIRDPCAG PVCDCKRNSD VMDCVILDDG GFLLMANHDD YTNQIGRFFG EIDPSLMRHL VNISVYAFNK SYDYQSVCEP GAAPKQGAG HRSAYVPSVA DILQIGWWAT AAAWSILQQF LLSLTFPRLL EAVEMEDDDF TASLSKQSCI TEQTQYFFDN D SKSFSGVL DCGNCSRIFH GEKLMNTNLI FIMVESKGTC PCDTRLLIQA EQTSDGPNPC DMVKQPRYRK GPDVCFDNNV LE DYTDCGG VSGLNPSLWY IIGIQFLLLW LVSGSTHRLL |
-Macromolecule #3: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.799594 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MVQKTSMSRG PYPPSQEIPM EVFDPSPQGK YSKRKGRFKR SDGSTSSDTT SNSFVRQGSA ESYTSRPSDS DVSLEEDREA LRKEAERQA LAQLEKAKTK PVAFAVRTNV GYNPSPGDEV PVQGVAITFE PKDFLHIKEK YNNDWWIGRL VKEGCEVGFI P SPVKLDSL ...String: MVQKTSMSRG PYPPSQEIPM EVFDPSPQGK YSKRKGRFKR SDGSTSSDTT SNSFVRQGSA ESYTSRPSDS DVSLEEDREA LRKEAERQA LAQLEKAKTK PVAFAVRTNV GYNPSPGDEV PVQGVAITFE PKDFLHIKEK YNNDWWIGRL VKEGCEVGFI P SPVKLDSL RLLQEQKLRQ NRLGSSKSGD NSSSSLGDVV TGTRRPTPPA SAKQKQKSTE HVPPYDVVPS MRPIILVGPS LK GYEVTDM MQKALFDFLK HRFDGRISIT RVTADISLAK RSVLNNPSKH IIIERSNTRS SLAEVQSEIE RIFELARTLQ LVA LDADTI NHPAQLSKTS LAPIIVYIKI TSPKVLQRLI KSRGKSQSKH LNVQIAASEK LAQCPPEMFD IILDENQLED ACEH LAEYL EAYWKATHPP SSTPPNPLLN RTMATAALAA SPAPVSNLQG PYLASGDQPL ERATGEHASM HEYPGELGQP PGLYP SSHP PGRAGTLRAL SRQDTFDADT PGSRNSAYTE LGDSCVDMET DPSEGPGLGD PAGGGTPPAR QGSWEDEEED YEEELT DNR NRGRNKARYC AEGGGPVLGR NKNELEGWGR GVYIR |
-Macromolecule #6: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: Y01 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 486.726 Da |
| Chemical component information | 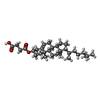 ChemComp-Y01: |
-Macromolecule #7: HEXADECANE
| Macromolecule | Name: HEXADECANE / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 7 / Formula: R16 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 226.441 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-R16: |
-Macromolecule #8: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine
| Macromolecule | Name: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: 3PE |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 748.065 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-3PE: |
-Macromolecule #9: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 9 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #10: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 10 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information | 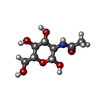 ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| Details | This sample was obtained from the monodispersed peak fractions of the size-exclusion chromatography. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 7676 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 7420 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-32 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 2097 / Average exposure time: 6.7 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Particle selection | Number selected: 787518 |
|---|---|
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL In silico model: The insilico model was generated using the ab-initio reconstruction in cryoSPARC. |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 3.3.1) |
| Final 3D classification | Number classes: 6 / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 3.1) |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 3.3.1) |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 3.3.1) / Number images used: 257473 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















 Z
Z Y
Y X
X