[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-33127: Cryo-EM structure of Dot1L and H2BK34ub-H3K79Nle nucleosome 2:1 c... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
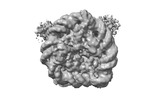
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Dot1L and H2BK34ub-H3K79Nle nucleosome 2:1 complex | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / histone H3K79 trimethyltransferase activity / [histone H3]-lysine79 N-trimethyltransferase / histone H3K79 methyltransferase activity / regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / Evasion by RSV of host interferon responses / female meiosis I / regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / histone H3 methyltransferase activity ...: / histone H3K79 trimethyltransferase activity / [histone H3]-lysine79 N-trimethyltransferase / histone H3K79 methyltransferase activity / regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / Evasion by RSV of host interferon responses / female meiosis I / regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / histone H3 methyltransferase activity / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / fat pad development / female gonad development /  histone methyltransferase activity / seminiferous tubule development / male meiosis I / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / heterochromatin formation / histone methyltransferase activity / seminiferous tubule development / male meiosis I / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / heterochromatin formation /  energy homeostasis / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Signaling by ALK fusions and activated point mutants / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / energy homeostasis / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Signaling by ALK fusions and activated point mutants / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway /  Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / telomere organization / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Regulation of PTEN localization / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / telomere organization / Pexophagy / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Regulation of PTEN localization / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus /  Regulation of BACH1 activity / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Translesion synthesis by POLK / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Josephin domain DUBs / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Translesion synthesis by POLK / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Josephin domain DUBs /  DNA methylation / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / neuron projection morphogenesis / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / HCMV Late Events / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / DNA methylation / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / neuron projection morphogenesis / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / HCMV Late Events / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C /  innate immune response in mucosa / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway innate immune response in mucosa / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathwaySimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.72 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.72 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ai HS / Liu AJ / Lou ZY / Liu L | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 5 items China, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2022Title: H2B Lys34 Ubiquitination Induces Nucleosome Distortion to Stimulate Dot1L Activity. Authors: Huasong Ai / Maoshen Sun / Aijun Liu / Zixian Sun / Tingting Liu / Lin Cao / Lujun Liang / Qian Qu / Zichen Li / Zhiheng Deng / Zebin Tong / Guochao Chu / Xiaolin Tian / Haiteng Deng / Suwen ...Authors: Huasong Ai / Maoshen Sun / Aijun Liu / Zixian Sun / Tingting Liu / Lin Cao / Lujun Liang / Qian Qu / Zichen Li / Zhiheng Deng / Zebin Tong / Guochao Chu / Xiaolin Tian / Haiteng Deng / Suwen Zhao / Jia-Bin Li / Zhiyong Lou / Lei Liu /  Abstract: Ubiquitination-dependent histone crosstalk plays critical roles in chromatin-associated processes and is highly associated with human diseases. Mechanism studies of the crosstalk have been of the ...Ubiquitination-dependent histone crosstalk plays critical roles in chromatin-associated processes and is highly associated with human diseases. Mechanism studies of the crosstalk have been of the central focus. Here our study on the crosstalk between H2BK34ub and Dot1L-catalyzed H3K79me suggests a novel mechanism of ubiquitination-induced nucleosome distortion to stimulate the activity of an enzyme. We determined the cryo-electron microscopy structures of Dot1L-H2BK34ub nucleosome complex and the H2BK34ub nucleosome alone. The structures reveal that H2BK34ub induces an almost identical orientation and binding pattern of Dot1L on nucleosome as H2BK120ub, which positions Dot1L for the productive conformation through direct ubiquitin-enzyme contacts. However, H2BK34-anchored ubiquitin does not directly interact with Dot1L as occurs in the case of H2BK120ub, but rather induces DNA and histone distortion around the modified site. Our findings establish the structural framework for understanding the H2BK34ub-H3K79me trans-crosstalk and highlight the diversity of mechanisms for histone ubiquitination to activate chromatin-modifying enzymes. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33127.map.gz emd_33127.map.gz | 59.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33127-v30.xml emd-33127-v30.xml emd-33127.xml emd-33127.xml | 23.3 KB 23.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33127.png emd_33127.png | 43.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33127_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33127_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33127_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33127_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.6 MB 59.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33127 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33127 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33127 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33127 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7xctMC  7xcrC  7xd0C  7xd1C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33127.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33127.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_33127_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_33127_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Complex of Dot1L(1-416) and H2BK34ub 2:1 nucleosome
+Supramolecule #1: Complex of Dot1L(1-416) and H2BK34ub 2:1 nucleosome
+Macromolecule #1: Ubiquitin
+Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A
+Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-K
+Macromolecule #5: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase, H3 lysine-79 specific
+Macromolecule #6: Histone domain-containing protein
+Macromolecule #7: DNA (145-MER)
+Macromolecule #8: DNA (145-MER)
+Macromolecule #9: S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 2.56 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
|---|---|
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.72 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 98100 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

































 Z
Z Y
Y X
X