+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
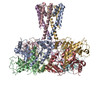
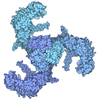
| Title | TpeA bound closed MthK-A88F mutant in nanodisc | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MTHK /  TRANSPORT PROTEIN / TRANSPORT PROTEIN /  ION CHANNEL / Blocker TpeA / ION CHANNEL / Blocker TpeA /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmonoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / potassium ion transport / identical protein binding /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  plasma membrane plasma membraneSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |    Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (archaea) Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (archaea) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.88 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.88 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Agarwal S / Nimigean CM | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Ball-and-chain inactivation in a calcium-gated potassium channel. Authors: Chen Fan / Nattakan Sukomon / Emelie Flood / Jan Rheinberger / Toby W Allen / Crina M Nimigean /    Abstract: Inactivation is the process by which ion channels terminate ion flux through their pores while the opening stimulus is still present. In neurons, inactivation of both sodium and potassium channels is ...Inactivation is the process by which ion channels terminate ion flux through their pores while the opening stimulus is still present. In neurons, inactivation of both sodium and potassium channels is crucial for the generation of action potentials and regulation of firing frequency. A cytoplasmic domain of either the channel or an accessory subunit is thought to plug the open pore to inactivate the channel via a 'ball-and-chain' mechanism. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to identify the molecular gating mechanism in calcium-activated potassium channels by obtaining structures of the MthK channel from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum-a purely calcium-gated and inactivating channel-in a lipid environment. In the absence of Ca, we obtained a single structure in a closed state, which was shown by atomistic simulations to be highly flexible in lipid bilayers at ambient temperature, with large rocking motions of the gating ring and bending of pore-lining helices. In Ca-bound conditions, we obtained several structures, including multiple open-inactivated conformations, further indication of a highly dynamic protein. These different channel conformations are distinguished by rocking of the gating rings with respect to the transmembrane region, indicating symmetry breakage across the channel. Furthermore, in all conformations displaying open channel pores, the N terminus of one subunit of the channel tetramer sticks into the pore and plugs it, with free energy simulations showing that this is a strong interaction. Deletion of this N terminus leads to functionally non-inactivating channels and structures of open states without a pore plug, indicating that this previously unresolved N-terminal peptide is responsible for a ball-and-chain inactivation mechanism. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_29605.map.gz emd_29605.map.gz | 3.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-29605-v30.xml emd-29605-v30.xml emd-29605.xml emd-29605.xml | 20.5 KB 20.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_29605_fsc.xml emd_29605_fsc.xml | 9.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_29605.png emd_29605.png | 52.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_29605_msk_1.map emd_29605_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-29605.cif.gz emd-29605.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_29605_additional_1.map.gz emd_29605_additional_1.map.gz emd_29605_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29605_half_map_1.map.gz emd_29605_half_map_2.map.gz emd_29605_half_map_2.map.gz | 45.4 MB 45.7 MB 45.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29605 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29605 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29605 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29605 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8fz7MC  9405C  9406C  9407C  5bkiC  5bkjC  5bkkC  8djbC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_29605.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_29605.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0826 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_29605_msk_1.map emd_29605_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_29605_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_29605_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_29605_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : TpeA bound MthK A88F mutant in 0 Ca2+
| Entire | Name: TpeA bound MthK A88F mutant in 0 Ca2+ |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: TpeA bound MthK A88F mutant in 0 Ca2+
| Supramolecule | Name: TpeA bound MthK A88F mutant in 0 Ca2+ / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (archaea) Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (archaea) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 220 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Calcium-gated potassium channel MthK
| Macromolecule | Name: Calcium-gated potassium channel MthK / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 8 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:    Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (archaea) Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (archaea) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 37.432258 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MVLVIEIIRK HLPRVLKVPA TRILLLVLAV IIYGTAGFHF IEGESWTVSL YWTFVTIATV GYGDYSPSTP LGMYFTVTLI VLGIGTFFV AVERLLEFLI NREQMKLMGL IDVAKSRHVV ICGWSESTLE CLRELRGSEV FVLAEDENVR KKVLRSGANF V HGDPTRVS ...String: MVLVIEIIRK HLPRVLKVPA TRILLLVLAV IIYGTAGFHF IEGESWTVSL YWTFVTIATV GYGDYSPSTP LGMYFTVTLI VLGIGTFFV AVERLLEFLI NREQMKLMGL IDVAKSRHVV ICGWSESTLE CLRELRGSEV FVLAEDENVR KKVLRSGANF V HGDPTRVS DLEKANVRGA RAVIVDLESD SETIHCILGI RKIDESVRII AEAERYENIE QLRMAGADQV ISPFVISGRL MS RSIDDGY EAMFVQDVLA EESTRRMVEV PIPEGSKLEG VSVLDADIHD VTGVIIIGVG RGDELIIDPP RDYSFRAGDI ILG IGKPEE IERLKNYISA UniProtKB: Calcium-gated potassium channel MthK |
-Macromolecule #2: (1R)-2-{[(S)-{[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl]o...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1R)-2-{[(S)-{[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-1-[(hexadecanoyloxy)methyl]ethyl (9Z)-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: PGW |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 749.007 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: 1-(tripentyl-$l^{4}-azanyl)pentane
| Macromolecule | Name: 1-(tripentyl-$l^{4}-azanyl)pentane / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: YQ1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 298.57 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-YQ1: |
-Macromolecule #4: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 7 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8.5 |
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: GOLD / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 80 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: BLOTTING FOR 2 S (BLOT FORCE 0). |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 58.9 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z
Z Y
Y X
X