[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-29004: Structure of the human L-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the human L-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.2 complexed with gabapentin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | CaV1.2_GBN_composite_map_DLM | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  voltage-gated calcium channel / CaV alpha2delta / voltage-gated calcium channel / CaV alpha2delta /  drug binding / drug binding /  gabapentin / gabapentin /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information : / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / : / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential /  immune system development / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential / positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity ... immune system development / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential / positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity ... : / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / : / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential /  immune system development / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential / positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity / cardiac conduction / immune system development / positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential / positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity / cardiac conduction /  L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / camera-type eye development / NCAM1 interactions / embryonic forelimb morphogenesis / calcium ion transport into cytosol / cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / camera-type eye development / NCAM1 interactions / embryonic forelimb morphogenesis / calcium ion transport into cytosol / cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction /  voltage-gated calcium channel complex / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / alpha-actinin binding / calcium channel regulator activity / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / alpha-actinin binding / calcium channel regulator activity / calcium ion import across plasma membrane /  voltage-gated calcium channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion /  T-tubule / Regulation of insulin secretion / calcium ion transmembrane transport / postsynaptic density membrane / T-tubule / Regulation of insulin secretion / calcium ion transmembrane transport / postsynaptic density membrane /  calcium channel activity / Z disc / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / calcium channel activity / Z disc / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion /  heart development / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / heart development / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration /  perikaryon / perikaryon /  postsynaptic density / postsynaptic density /  calmodulin binding / calmodulin binding /  dendrite / dendrite /  membrane / membrane /  metal ion binding / metal ion binding /  plasma membrane / plasma membrane /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) | |||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen Z / Mondal A / Minor DL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis for Caαδ:gabapentin binding. Authors: Zhou Chen / Abhisek Mondal / Daniel L Minor /  Abstract: Gabapentinoid drugs for pain and anxiety act on the Caαδ-1 and Caαδ-2 subunits of high-voltage-activated calcium channels (Ca1s and Ca2s). Here we present the cryo-EM structure of the gabapentin- ...Gabapentinoid drugs for pain and anxiety act on the Caαδ-1 and Caαδ-2 subunits of high-voltage-activated calcium channels (Ca1s and Ca2s). Here we present the cryo-EM structure of the gabapentin-bound brain and cardiac Ca1.2/Caβ/Caαδ-1 channel. The data reveal a binding pocket in the Caαδ-1 dCache1 domain that completely encapsulates gabapentin and define Caαδ isoform sequence variations that explain the gabapentin binding selectivity of Caαδ-1 and Caαδ-2. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_29004.map.gz emd_29004.map.gz | 258.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-29004-v30.xml emd-29004-v30.xml emd-29004.xml emd-29004.xml | 21.5 KB 21.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_29004.png emd_29004.png | 115.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29004 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29004 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29004 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-29004 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8fd7MC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_29004.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_29004.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | CaV1.2_GBN_composite_map_DLM | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.835 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Ternary complex of human CaV alpha1C with rabbit CaV alpha2delta-...
+Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of human CaV alpha1C with rabbit CaV alpha2delta-...
+Supramolecule #2: Human CaV alpha1C
+Supramolecule #3: Rabbit CaV alpha2delta-1
+Supramolecule #4: Rabbit CaV beta3
+Macromolecule #1: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
+Macromolecule #2: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C
+Macromolecule #3: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-3
+Macromolecule #5: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
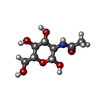
+Macromolecule #6: [1-(AMINOMETHYL)CYCLOHEXYL]ACETIC ACID
+Macromolecule #7: CALCIUM ION
+Macromolecule #8: SODIUM ION
+Macromolecule #9: (2R)-3-{[(R)-(2-aminoethoxy)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-2-(dodecanoy...
+Macromolecule #10: (2S)-3-{[(R)-(2-aminoethoxy)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-2-(dodecanoy...
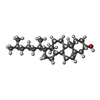
+Macromolecule #11: CHOLESTEROL
+Macromolecule #12: water
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.0 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 46.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 259107 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller