[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
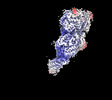
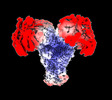
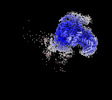
Yorodumi- EMDB-27421: Avs3 bound to phage PhiV-1 terminase, C2 refinement of Cap4 nucle... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Avs3 bound to phage PhiV-1 terminase, C2 refinement of Cap4 nuclease domain | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Avs3 bound to gp19 terminase, C2 refinement of Cap4 nuclease domain | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | phage defense / pattern-recognition receptor / nlr / stand /  atpase / atpase /  ANTIVIRAL PROTEIN ANTIVIRAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationchromosome organization => GO:0051276 / viral terminase, large subunit / viral DNA genome packaging /  Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds; Endodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds; Endodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement /  endonuclease activity / endonuclease activity /  ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP hydrolysis activity /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Salmonella enterica (bacteria) / Salmonella enterica (bacteria) /  Escherichia phage PhiV-1 (virus) Escherichia phage PhiV-1 (virus) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wilkinson ME / Gao L / Strecker J / Makarova KS / Macrae RK / Koonin EV / Zhang F | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2022 Journal: Science / Year: 2022Title: Prokaryotic innate immunity through pattern recognition of conserved viral proteins. Authors: Linyi Alex Gao / Max E Wilkinson / Jonathan Strecker / Kira S Makarova / Rhiannon K Macrae / Eugene V Koonin / Feng Zhang /  Abstract: Many organisms have evolved specialized immune pattern-recognition receptors, including nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs) of the STAND superfamily that are ubiquitous in ...Many organisms have evolved specialized immune pattern-recognition receptors, including nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs) of the STAND superfamily that are ubiquitous in plants, animals, and fungi. Although the roles of NLRs in eukaryotic immunity are well established, it is unknown whether prokaryotes use similar defense mechanisms. Here, we show that antiviral STAND (Avs) homologs in bacteria and archaea detect hallmark viral proteins, triggering Avs tetramerization and the activation of diverse N-terminal effector domains, including DNA endonucleases, to abrogate infection. Cryo-electron microscopy reveals that Avs sensor domains recognize conserved folds, active-site residues, and enzyme ligands, allowing a single Avs receptor to detect a wide variety of viruses. These findings extend the paradigm of pattern recognition of pathogen-specific proteins across all three domains of life. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
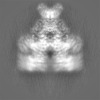
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27421.map.gz emd_27421.map.gz | 166 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27421-v30.xml emd-27421-v30.xml emd-27421.xml emd-27421.xml | 19.3 KB 19.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27421_fsc.xml emd_27421_fsc.xml | 12.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_27421.png emd_27421.png | 92.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_27421_msk_1.map emd_27421_msk_1.map | 178 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27421.cif.gz emd-27421.cif.gz | 7.3 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27421_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27421_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27421_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27421_half_map_2.map.gz | 139.1 MB 139.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27421 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27421 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27421 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27421 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 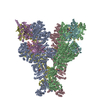 8dgcMC  8dgfC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27421.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27421.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Avs3 bound to gp19 terminase, C2 refinement of Cap4 nuclease domain | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.8697 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_27421_msk_1.map emd_27421_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
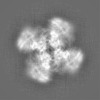
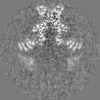
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
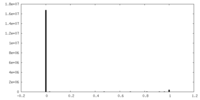
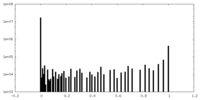
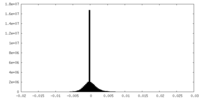
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 1
| File | emd_27421_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 2
| File | emd_27421_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Avs3 bound to phage PhiV-1 terminase
| Entire | Name: Avs3 bound to phage PhiV-1 terminase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Avs3 bound to phage PhiV-1 terminase
| Supramolecule | Name: Avs3 bound to phage PhiV-1 terminase / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.21 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: SeAvs3
| Macromolecule | Name: SeAvs3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Salmonella enterica (bacteria) Salmonella enterica (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 236.796469 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MSDSLLVRTS RDGDQFHYLW AARRALRLLE PQSTLVALTI EGASTTEMGS QPVVEDGEEL IDIAEYYGSN ELATATTVRY MQLKHSTMH SDTPFPPSGL QKTIEGFATR YKALIQKIPV ETLRTKLEFW FVTNRPVSSS FSEAINDAAN QHVTRHPHDL A KLEKFTGL ...String: MSDSLLVRTS RDGDQFHYLW AARRALRLLE PQSTLVALTI EGASTTEMGS QPVVEDGEEL IDIAEYYGSN ELATATTVRY MQLKHSTMH SDTPFPPSGL QKTIEGFATR YKALIQKIPV ETLRTKLEFW FVTNRPVSSS FSEAINDAAN QHVTRHPHDL A KLEKFTGL QGAELSIFCQ LLHIEGQQDD LWSQRNILLR ESAGYLPDLD TEAPLKLKEL VNRKALTESA ANPSITRMDV LR ALGVDET DLFPAPCRIE RIENSVSRTQ EATLVQRVVE AFGAPVIIHA DAGVGKSIFS THIEEHLPTG SVSILYDCFG LGQ YRNASS YRHHHRTALV QMANEMASRG LCHPLIPNAG TGISQYMRAF LHRLSQSISI LRASEPLAVL CIIIDAADNA QMAA EEIGE TRSFIKDLIR EKLPDGVCLV ALCRPYRREL LDPPPEALTL SLQTFNRDET AAHLHQKFPD ASESDVDEFH RLSSC NPRV QALSLSQNLP LNDTLRLLGP NPKTVEDTIG EVLEKSIARL RDTAGISERA QIDTICSALA ILRPLIPLSV LSAISG VAG SAIKSFALDL GRPLIVSGET IQFFDEPAET WFQRRFRPSA ADLHQFITKL RPLTKDSSYA ASVLPALMLE GNQLSEL IE LAISSQALPE TSAVERRDIE LQRLQFALKA ALRTGRYQDA AKLALKAGGE CAGDNRQRVL LRDNIDLAAK FVGSNGVQ E LVSRNAFPDT GWPGSRNAYY AAILSEYPEL SGEARSRLRL TMEWLTNWSQ LPDDERSRQN VTDQDRAVML IACLNIHGA EAAARELRRW RPRKLSFDAG KIVAMQLLAH ARYDELDQLA IAAGNDISLV MGIVLEARKL HRPVAEQAIR RTWRLLKSQR VSIKDRNHA NNQTIAAITG MVEMALIQSV CTESESIQLL DRYLPKVPPY ALTSEYSKER VAYVRAYALQ ANLMGSQLAL S DLASTEVK KELMAEKRHG ESDDLRQLKQ YSGVLIPWYN LWAKVILGKT RKADLESELS DTQKESTAIK GHSYSEHSLS SN EIANVWF DILIEAGNVS KDDVENIIKW SQHKGNRVFT PTLHRFSSVC AEISGLGELS YHFAELALSL WRDEHSDAQI KAD GYIDLS RSLISLDEPE AKEYFNQAIE VTNKLGDENL SRWEAILDLA EYVAGKTQVP PEISYKLARC AELTREYVDR DKHF AWSDT VEILAELCPS SALAIISRWR DRTFGNHRSI LAWTIEHLVK KNKINALDAL PLITFENDWH KCDLLDSVLS SCTDD KDKI MAFEVVYHYT KFNVQNIQNL KKLDAISTSL GIEHTELKER ISGLQHTETV SKKSSLSSND NEQGHDQEWE SIFKDC DLS SIDGISAAYE KFRNVPEFYS KETFIKKAIS RVKTGKECSF ITAIGAIFHW GLYDFKYILE SIPDEWTSRL SIKTTLA GL IKEYCQRFCM RIRKSRVYEI FPFSLASRLS GISEKEIFGI TLEAIAESPE PANSDRLFSL PGLLVSKLES NEALDVLS Y ALDLFDEVLK DEDGDGPWNE KLSPPTHVED SLAGYIWARL GSPEAEMRWQ AAHAVLALCR MSRTCVIQGI FQHAINATT LPFCDRNLPF YTLHAQLWLM IAAARVALDD GKSLIPNIGY FYHYATTDQP HVLIRHFAAR TLLALHDSDL ISIPAQEENK LRNINQSTT LPVLDKVEDH RGEDSYTFGI DFGPYWLKPL GRCFGVSQKQ LEPEMLRIIR DVLGFKGSRN WDEDERNKRR Y YQDRDNHH SHGSYPRVDD YHFYLSYHAM FMTAGQLLAT KPLVGSDYDD VEDVFQDWLR RHDISRNDHR WLADRRDIPP KE RSSWLNS SSDNRDEWLA SISENVFNET LCPSPGLLTL WGRWSDVCSD RKESIIVHSA LVSPERSLSL LRALQTTKNV YDY KIPDAG DNLEIDHAHY QLKGWIKDIA EYCGIDEFDP WAGNVRFPIP EPASFIIDAM KLTTDKDHRV WYSPSDVEPA MISS IWGHL SGKNDEEKSH GYRLCASIHF IKSALETFNM DLILEVDVDR YSRNSRYERN NENELDNIPS STRLFLFRHD GTIHT LYGN YRNGEKTS |
-Macromolecule #2: Terminase, large subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: Terminase, large subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number:  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Escherichia phage PhiV-1 (virus) Escherichia phage PhiV-1 (virus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 66.345469 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MSQSQEAKNA LIIAQLKGDF VAFLFVLWKA LNLPKPTKCQ IDMARTLANG DHKKFILQAF RGIGKSFITC AFVVWVLWRD PQLKVLIVS ASKERADANS IFIKNIIDLL PFLSELKPRP GQRDSVISFD VGLAKPDHSP SVKSVGITGQ LTGSRADIII A DDVEVPGN ...String: MSQSQEAKNA LIIAQLKGDF VAFLFVLWKA LNLPKPTKCQ IDMARTLANG DHKKFILQAF RGIGKSFITC AFVVWVLWRD PQLKVLIVS ASKERADANS IFIKNIIDLL PFLSELKPRP GQRDSVISFD VGLAKPDHSP SVKSVGITGQ LTGSRADIII A DDVEVPGN SSTSSAREKL WTLVTEFAAL LKPLPTSRVI YLGTPQTEMT LYKELEDNKG YSTVIWPAQY PRNDAEALYY GD RLAPMLK AEYDEGFELL RGQPTDPVRF DMDDLREREL EYGKAGYTLQ FMLNPNLSDA EKYPLRLRDA IVCAVDPERA PLS YQWLPN RQNRNEELPN VGLKGDDIHA FHTCSSRTAE YQSKILVIDP SGRGKDETGY AVLYSLNGYI YLMEVGGFRG GYDD ATLEK LAKKAKQWKV QTVVHESNFG DGMFGKIFSP ILLKHHKCAL EEIRAKGMKE MRICDTIEPL MGAHKLVIRD EVIRE DYQT ARDLDGKHDV RYSAFYQMTR MTRERGAVAH DDRIDAIALG IEYLREGMLV DSRVGEEEMT LEFLEHHMEK QTIGGD QIH SFDVGGVDIY YEDEDGGSSF IEW UniProtKB: Terminase, large subunit |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information | 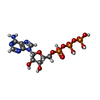 ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 30.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z
Z Y
Y X
X