[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-17155: Cryo-EM structure of CLOCK-BMAL1 bound to a nucleosomal E-box at ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
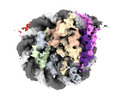
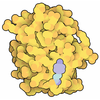
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of CLOCK-BMAL1 bound to a nucleosomal E-box at position SHL-6.2 (DNA conformation 1) | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Local resolution filtered map. | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  E-box / E-box /  transcription factor / transcription factor /  circadian clock / circadian clock /  GENE REGULATION GENE REGULATION | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCLOCK-BMAL transcription complex / positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell differentiation /  regulation of hair cycle / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / positive regulation of protein acetylation / negative regulation of glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway / maternal process involved in parturition / regulation of type B pancreatic cell development / bHLH transcription factor binding / regulation of hair cycle / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / positive regulation of protein acetylation / negative regulation of glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway / maternal process involved in parturition / regulation of type B pancreatic cell development / bHLH transcription factor binding /  regulation of cellular senescence ...CLOCK-BMAL transcription complex / positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell differentiation / regulation of cellular senescence ...CLOCK-BMAL transcription complex / positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell differentiation /  regulation of hair cycle / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / positive regulation of protein acetylation / negative regulation of glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway / maternal process involved in parturition / regulation of type B pancreatic cell development / bHLH transcription factor binding / regulation of hair cycle / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / positive regulation of protein acetylation / negative regulation of glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway / maternal process involved in parturition / regulation of type B pancreatic cell development / bHLH transcription factor binding /  regulation of cellular senescence / perichromatin fibrils / regulation of cellular senescence / perichromatin fibrils /  aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex / aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex /  chromatoid body / negative regulation of TOR signaling / positive regulation of circadian rhythm / oxidative stress-induced premature senescence / negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / response to redox state / negative regulation of fat cell differentiation / chromatoid body / negative regulation of TOR signaling / positive regulation of circadian rhythm / oxidative stress-induced premature senescence / negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / response to redox state / negative regulation of fat cell differentiation /  protein acetylation / regulation of protein catabolic process / protein acetylation / regulation of protein catabolic process /  E-box binding / E-box binding /  aryl hydrocarbon receptor binding / regulation of insulin secretion / aryl hydrocarbon receptor binding / regulation of insulin secretion /  regulation of neurogenesis / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / regulation of neurogenesis / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Packaging Of Telomere Ends /  histone acetyltransferase activity / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / histone acetyltransferase activity / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere /  histone acetyltransferase / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / telomere organization / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Interleukin-7 signaling / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / histone acetyltransferase / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Meiotic synapsis / telomere organization / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Interleukin-7 signaling / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins /  DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / HCMV Late Events / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / HCMV Late Events /  innate immune response in mucosa / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / Defective pyroptosis / cellular response to ionizing radiation / HDACs deacetylate histones / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / innate immune response in mucosa / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / Defective pyroptosis / cellular response to ionizing radiation / HDACs deacetylate histones / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape /  lipopolysaccharide binding / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / circadian regulation of gene expression / lipopolysaccharide binding / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / circadian regulation of gene expression /  Hsp90 protein binding / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / Hsp90 protein binding / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression /  regulation of circadian rhythm / HDMs demethylate histones / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / PML body / Metalloprotease DUBs / chromatin DNA binding / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / RMTs methylate histone arginines / regulation of circadian rhythm / HDMs demethylate histones / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / PML body / Metalloprotease DUBs / chromatin DNA binding / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / RMTs methylate histone arginines /  Meiotic recombination / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation /  autophagy / autophagy /  nucleosome assembly / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / HCMV Early Events / positive regulation of inflammatory response / protein import into nucleus / nucleosome assembly / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / HCMV Early Events / positive regulation of inflammatory response / protein import into nucleus /  circadian rhythm / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / structural constituent of chromatin / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / UCH proteinases / circadian rhythm / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / structural constituent of chromatin / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / UCH proteinases /  nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs /  chromosome / chromosome /  gene expression gene expressionSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) / Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) /   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 6.2 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 6.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Michael AK / Stoos L / Kempf G / Cavadini S / Thoma NH | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Switzerland, Switzerland,  France, 5 items France, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Cooperation between bHLH transcription factors and histones for DNA access. Authors: Alicia K Michael / Lisa Stoos / Priya Crosby / Nikolas Eggers / Xinyu Y Nie / Kristina Makasheva / Martina Minnich / Kelly L Healy / Joscha Weiss / Georg Kempf / Simone Cavadini / Lukas ...Authors: Alicia K Michael / Lisa Stoos / Priya Crosby / Nikolas Eggers / Xinyu Y Nie / Kristina Makasheva / Martina Minnich / Kelly L Healy / Joscha Weiss / Georg Kempf / Simone Cavadini / Lukas Kater / Jan Seebacher / Luca Vecchia / Deyasini Chakraborty / Luke Isbel / Ralph S Grand / Florian Andersch / Jennifer L Fribourgh / Dirk Schübeler / Johannes Zuber / Andrew C Liu / Peter B Becker / Beat Fierz / Carrie L Partch / Jerome S Menet / Nicolas H Thomä /     Abstract: The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family of transcription factors recognizes DNA motifs known as E-boxes (CANNTG) and includes 108 members. Here we investigate how chromatinized E-boxes are engaged ...The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family of transcription factors recognizes DNA motifs known as E-boxes (CANNTG) and includes 108 members. Here we investigate how chromatinized E-boxes are engaged by two structurally diverse bHLH proteins: the proto-oncogene MYC-MAX and the circadian transcription factor CLOCK-BMAL1 (refs. ). Both transcription factors bind to E-boxes preferentially near the nucleosomal entry-exit sites. Structural studies with engineered or native nucleosome sequences show that MYC-MAX or CLOCK-BMAL1 triggers the release of DNA from histones to gain access. Atop the H2A-H2B acidic patch, the CLOCK-BMAL1 Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) dimerization domains engage the histone octamer disc. Binding of tandem E-boxes at endogenous DNA sequences occurs through direct interactions between two CLOCK-BMAL1 protomers and histones and is important for circadian cycling. At internal E-boxes, the MYC-MAX leucine zipper can also interact with histones H2B and H3, and its binding is indirectly enhanced by OCT4 elsewhere on the nucleosome. The nucleosomal E-box position and the type of bHLH dimerization domain jointly determine the histone contact, the affinity and the degree of competition and cooperativity with other nucleosome-bound factors. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_17155.map.gz emd_17155.map.gz | 113.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-17155-v30.xml emd-17155-v30.xml emd-17155.xml emd-17155.xml | 29.3 KB 29.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_17155_fsc.xml emd_17155_fsc.xml | 12.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_17155.png emd_17155.png | 71.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_17155_additional_1.map.gz emd_17155_additional_1.map.gz emd_17155_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17155_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17155_half_map_2.map.gz emd_17155_half_map_2.map.gz | 136.1 MB 136.2 MB 136.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17155 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17155 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17155 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17155 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8osjMC 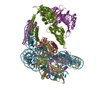 8oskC  8oslC  8otsC  8ottC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_17155.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 172.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_17155.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 172.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Local resolution filtered map. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.68 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Unfiltered map.
| File | emd_17155_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered map. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-map B.
| File | emd_17155_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-map B. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half-map A.
| File | emd_17155_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half-map A. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : CLOCK-BMAL1 bound to a nucleosome at SHL -6.2
+Supramolecule #1: CLOCK-BMAL1 bound to a nucleosome at SHL -6.2
+Supramolecule #2: Nucleosome core particle
+Supramolecule #3: Histone octamer
+Supramolecule #4: Nucleosomal DNA
+Supramolecule #5: CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer
+Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.1
+Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
+Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-J
+Macromolecule #7: Circadian locomoter output cycles protein kaput
+Macromolecule #8: Basic helix-loop-helix ARNT-like protein 1
+Macromolecule #5: DNA (124-MER)
+Macromolecule #6: DNA (124-MER)
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.2 µm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.2 µm |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z
Z Y
Y X
X