+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Contributions of histone tail clipping and acetylation in nucleosome transcription by RNA polymerase II. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nucleic Acids Res, Vol. 51, Issue 19, Page 10364-10374, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Oct 27, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | Takumi Oishi / Suguru Hatazawa / Tomoya Kujirai / Junko Kato / Yuki Kobayashi / Mitsuo Ogasawara / Munetaka Akatsu / Haruhiko Ehara / Shun-Ichi Sekine / Gosuke Hayashi / Yoshimasa Takizawa / Hitoshi Kurumizaka /  |
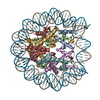
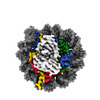
| PubMed Abstract | The N-terminal tails of histones protrude from the nucleosome core and are target sites for histone modifications, such as acetylation and methylation. Histone acetylation is considered to enhance ...The N-terminal tails of histones protrude from the nucleosome core and are target sites for histone modifications, such as acetylation and methylation. Histone acetylation is considered to enhance transcription in chromatin. However, the contribution of the histone N-terminal tail to the nucleosome transcription by RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) has not been clarified. In the present study, we reconstituted nucleosomes lacking the N-terminal tail of each histone, H2A, H2B, H3 or H4, and performed RNAPII transcription assays. We found that the N-terminal tail of H3, but not H2A, H2B and H4, functions in RNAPII pausing at the SHL(-5) position of the nucleosome. Consistently, the RNAPII transcription assay also revealed that the nucleosome containing N-terminally acetylated H3 drastically alleviates RNAPII pausing at the SHL(-5) position. In addition, the H3 acetylated nucleosome produced increased amounts of the run-off transcript. These results provide important evidence that the H3 N-terminal tail plays a role in RNAPII pausing at the SHL(-5) position of the nucleosome, and its acetylation directly alleviates this nucleosome barrier. |
 External links External links |  Nucleic Acids Res / Nucleic Acids Res /  PubMed:37718728 / PubMed:37718728 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.36 - 3.44 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-36389, PDB-8jl9: EMDB-36390, PDB-8jla: EMDB-36391, PDB-8jlb: EMDB-36393, PDB-8jld: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION/DNA /  nuclear protein / nuclear protein /  chromatin / GENE REGULATION-DNA COMPLEX chromatin / GENE REGULATION-DNA COMPLEX |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers