+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | G-protein activation by a metabotropic glutamate receptor. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 595, Issue 7867, Page 450-454, Year 2021 |
| Publish date | Jun 30, 2021 |
 Authors Authors | Alpay B Seven / Ximena Barros-Álvarez / Marine de Lapeyrière / Makaía M Papasergi-Scott / Michael J Robertson / Chensong Zhang / Robert M Nwokonko / Yang Gao / Justin G Meyerowitz / Jean-Philippe Rocher / Dominik Schelshorn / Brian K Kobilka / Jesper M Mathiesen / Georgios Skiniotis /    |
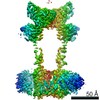
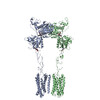
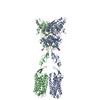
| PubMed Abstract | Family C G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) operate as obligate dimers with extracellular domains that recognize small ligands, leading to G-protein activation on the transmembrane (TM) domains of ...Family C G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) operate as obligate dimers with extracellular domains that recognize small ligands, leading to G-protein activation on the transmembrane (TM) domains of these receptors by an unknown mechanism. Here we show structures of homodimers of the family C metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 (mGlu2) in distinct functional states and in complex with heterotrimeric G. Upon activation of the extracellular domain, the two transmembrane domains undergo extensive rearrangement in relative orientation to establish an asymmetric TM6-TM6 interface that promotes conformational changes in the cytoplasmic domain of one protomer. Nucleotide-bound G can be observed pre-coupled to inactive mGlu2, but its transition to the nucleotide-free form seems to depend on establishing the active-state TM6-TM6 interface. In contrast to family A and B GPCRs, G-protein coupling does not involve the cytoplasmic opening of TM6 but is facilitated through the coordination of intracellular loops 2 and 3, as well as a critical contribution from the C terminus of the receptor. The findings highlight the synergy of global and local conformational transitions to facilitate a new mode of G-protein activation. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:34194039 / PubMed:34194039 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.2 - 3.65 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-23994, PDB-7mtq: EMDB-23995, PDB-7mtr: EMDB-23996, PDB-7mts: |
| Chemicals | 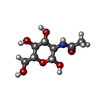 ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-Z99:  ChemComp-GLU:  ChemComp-ZQY: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  MEMBRANE PROTEIN/ANTAGONIST / Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 2 (mGlu2) (mGluR2) / Family C G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) / MEMBRANE PROTEIN/ANTAGONIST / Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 2 (mGlu2) (mGluR2) / Family C G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) /  Heterotrimeric G protein / CryoEM structure / Heterotrimeric G protein / CryoEM structure /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN-ANTAGONIST complex / MEMBRANE PROTEIN-ANTAGONIST complex /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN/AGONIST / MEMBRANE PROTEIN/AGONIST /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN-AGONIST complex / MEMBRANE PROTEIN-AGONIST complex /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN/SIGNALING PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN/SIGNALING PROTEIN /  MEMBRANE PROTEIN-SIGNALING PROTEIN complex MEMBRANE PROTEIN-SIGNALING PROTEIN complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers