[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-1950: 3D-Structure of tarantula myosin filament obtained by cryo-electr... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1950 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
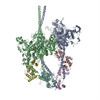
| Title | 3D-Structure of tarantula myosin filament obtained by cryo-electron microscopy | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | This is a density map of tarantula thick filaments, the initial view is from the Z line perspective, if the map is rotated by 90 degress in x direction, the J motif of the interacting heads features and the backbone subfilaments can be seen clearly | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  cryo-EM / cryo-EM /  thick filament / flexible docking / thick filament / flexible docking /  single particle reconstruction / Iterative Helical Real Space Reconstruction (IHRSR) / Myosin regulation / myosin regulatory light chain / single particle reconstruction / Iterative Helical Real Space Reconstruction (IHRSR) / Myosin regulation / myosin regulatory light chain /  phosphorylation phosphorylation | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmyosin II filament / regulation of slow-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction /  myofibril assembly / myofibril assembly /  elastic fiber assembly / elastic fiber assembly /  myosin light chain binding / skeletal muscle myosin thick filament assembly / muscle myosin complex / myosin light chain binding / skeletal muscle myosin thick filament assembly / muscle myosin complex /  myosin II binding / muscle filament sliding ...myosin II filament / regulation of slow-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction / myosin II binding / muscle filament sliding ...myosin II filament / regulation of slow-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction /  myofibril assembly / myofibril assembly /  elastic fiber assembly / elastic fiber assembly /  myosin light chain binding / skeletal muscle myosin thick filament assembly / muscle myosin complex / myosin light chain binding / skeletal muscle myosin thick filament assembly / muscle myosin complex /  myosin II binding / muscle filament sliding / regulation of the force of heart contraction / myosin II binding / muscle filament sliding / regulation of the force of heart contraction /  actomyosin / transition between fast and slow fiber / myosin filament / actomyosin structure organization / actomyosin / transition between fast and slow fiber / myosin filament / actomyosin structure organization /  myosin II complex / adult heart development / cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress / cardiac muscle cell development / myosin II complex / adult heart development / cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress / cardiac muscle cell development /  myosin complex / structural constituent of muscle / sarcomere organization / microfilament motor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / myosin complex / structural constituent of muscle / sarcomere organization / microfilament motor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis /  myofibril / myofibril /  myosin heavy chain binding / cytoskeletal motor activity / skeletal muscle contraction / smooth muscle contraction / striated muscle contraction / ATP metabolic process / myosin heavy chain binding / cytoskeletal motor activity / skeletal muscle contraction / smooth muscle contraction / striated muscle contraction / ATP metabolic process /  stress fiber / cardiac muscle contraction / stress fiber / cardiac muscle contraction /  regulation of heart rate / regulation of heart rate /  sarcomere / sarcomere /  muscle contraction / muscle contraction /  ADP binding / Z disc / ADP binding / Z disc /  actin filament binding / actin filament binding /  actin binding / actin binding /  calmodulin binding / calmodulin binding /  calcium ion binding / magnesium ion binding / calcium ion binding / magnesium ion binding /  ATP binding / ATP binding /  cytosol / cytosol /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Aphonopelma sp. (spider) Aphonopelma sp. (spider) | ||||||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction /  cryo EM / cryo EM /  negative staining / Resolution: 20.0 Å negative staining / Resolution: 20.0 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Alamo L / Wriggers W / Pinto A / Bartoli F / Salazar L / Zhao F / Craig R / Padron R | ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2008 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2008Title: Three-dimensional reconstruction of tarantula myosin filaments suggests how phosphorylation may regulate myosin activity. Authors: Lorenzo Alamo / Willy Wriggers / Antonio Pinto / Fulvia Bártoli / Leiria Salazar / Fa-Qing Zhao / Roger Craig / Raúl Padrón /  Abstract: Muscle contraction involves the interaction of the myosin heads of the thick filaments with actin subunits of the thin filaments. Relaxation occurs when this interaction is blocked by molecular ...Muscle contraction involves the interaction of the myosin heads of the thick filaments with actin subunits of the thin filaments. Relaxation occurs when this interaction is blocked by molecular switches on these filaments. In many muscles, myosin-linked regulation involves phosphorylation of the myosin regulatory light chains (RLCs). Electron microscopy of vertebrate smooth muscle myosin molecules (regulated by phosphorylation) has provided insight into the relaxed structure, revealing that myosin is switched off by intramolecular interactions between its two heads, the free head and the blocked head. Three-dimensional reconstruction of frozen-hydrated specimens revealed that this asymmetric head interaction is also present in native thick filaments of tarantula striated muscle. Our goal in this study was to elucidate the structural features of the tarantula filament involved in phosphorylation-based regulation. A new reconstruction revealed intra- and intermolecular myosin interactions in addition to those seen previously. To help interpret the interactions, we sequenced the tarantula RLC and fitted an atomic model of the myosin head that included the predicted RLC atomic structure and an S2 (subfragment 2) crystal structure to the reconstruction. The fitting suggests one intramolecular interaction, between the cardiomyopathy loop of the free head and its own S2, and two intermolecular interactions, between the cardiac loop of the free head and the essential light chain of the blocked head and between the Leu305-Gln327 interaction loop of the free head and the N-terminal fragment of the RLC of the blocked head. These interactions, added to those previously described, would help switch off the thick filament. Molecular dynamics simulations suggest how phosphorylation could increase the helical content of the RLC N-terminus, weakening these interactions, thus releasing both heads and activating the thick filament. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1950.map.gz emd_1950.map.gz | 46.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1950-v30.xml emd-1950-v30.xml emd-1950.xml emd-1950.xml | 15.7 KB 15.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  em-1950.jpg em-1950.jpg | 107.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1950 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1950 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1950 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1950 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3dtpMU  3jbhM M: atomic model generated by this map U: unfit; in different coordinate system*YM |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1950.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 58.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1950.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 58.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | This is a density map of tarantula thick filaments, the initial view is from the Z line perspective, if the map is rotated by 90 degress in x direction, the J motif of the interacting heads features and the backbone subfilaments can be seen clearly | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X: 2.48 Å / Y: 2.48 Å / Z: 2.482 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Myosin filaments from Tarantula striated muscle
| Entire | Name: Myosin filaments from Tarantula striated muscle |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Myosin filaments from Tarantula striated muscle
| Supramolecule | Name: Myosin filaments from Tarantula striated muscle / type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: Polymer of a multiple myosin assembled over a paramyosin core Number unique components: 2 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Myosin II
| Macromolecule | Name: Myosin II / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Myosin Type II / Oligomeric state: Polymer / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Aphonopelma sp. (spider) / synonym: Tarantula / Tissue: Muscle / Cell: Myofibrils / Location in cell: Sarcomere Aphonopelma sp. (spider) / synonym: Tarantula / Tissue: Muscle / Cell: Myofibrils / Location in cell: Sarcomere |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  negative staining, negative staining,  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 Details: 100mM NaCl,3mM MgCl2,1mM EGTA, 5mM PIPES, 5mM NaH2PO4,1mM NaN3. |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: A 6 ul aliquot of native purified tarantula thick filaments suspension (Hidalgo et al. 2001) was applied to a 400 mesh grid coated with a holey carbon film that had been rendered hydrophilic ...Details: A 6 ul aliquot of native purified tarantula thick filaments suspension (Hidalgo et al. 2001) was applied to a 400 mesh grid coated with a holey carbon film that had been rendered hydrophilic by glow discharge in n-amylamine vapor for 3 minutes before use. After allowing the filaments to adsorb to the grid for 30 seconds, the grid was rinsed with the relaxing rinse, then placed in a humidity chamber (aprox. 80% relative humidity). Blotting was performed from one side of the grid till a thin sample film on it using Whatman No 42 filter paper, then the grid was immediately plunged under gravity into liquid ethane cooled by liquid nitrogen. Grids were stored under liquid nitrogen. |
| Grid | Details: Holey carbon grids 400 mesh |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 93 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Details: Vitrification instrument: Home-made plunger. Blotting was performed from one side of the grid till a thin sample film on it using Whatman No 42 filter paper, then the grid was immediately ...Details: Vitrification instrument: Home-made plunger. Blotting was performed from one side of the grid till a thin sample film on it using Whatman No 42 filter paper, then the grid was immediately plunged under gravity into liquid ethane cooled by liquid nitrogen. Grids were stored under liquid nitrogen. Method: Plunging in a liquid ethane |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI/PHILIPS CM120T |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 120 kV / Electron source: LAB6 |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 35000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.95 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.95 µm / Nominal magnification: 35000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.95 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.95 µm / Nominal magnification: 35000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Eucentric / Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Temperature | Min: 88 K / Max: 90 K |
| Details | Holey carbon grids Cryo preserved in Liquid ethane were observed in a Philips CM120 electron microscope under low dose conditions. Only filaments on thin carbon over holes were photographed |
| Date | Oct 23, 2002 |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: OTHER / Digitization - Sampling interval: 8.47 µm / Number real images: 1008 / Bits/pixel: 14 |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 100 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: 30 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C4 (4 fold cyclic  ) )Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 20.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: SPIDER Details: Three-dimensional single particle reconstruction was carried out by a modification of the IHRSR method, using SPIDER. Low-dose electron micrographs of 1008 frozen-hydrated thick filaments ...Details: Three-dimensional single particle reconstruction was carried out by a modification of the IHRSR method, using SPIDER. Low-dose electron micrographs of 1008 frozen-hydrated thick filaments halves ere digitized at 0.248 nm per pixel using a Nikon Super Coolscan 8000 ED scanner. Filaments were aligned with the bare zone at the top, to ensure correct polarity in subsequent steps. A total of 15,504 segments, each 62 nm long, with an overlap of 55.8 nm, and containing aprox. 40,000 unique pairs of interacting myosin heads went into the reconstruction. As an initial reference model we used the tarantula negatively stained 3D-map, which was axially rotated, axially shifted and also out of plane tilted up to plus-minus12deg. for projection matching, giving a total of 4,095 projections (13 tilted projections plus-minus12deg. every 2deg., 45 reference rotated projections (0-90 degrees, 2deg. rotation angle), and 7 image axial shifts of 2.2 nm. The resulting 3D-map combines about 10,700 out of 15,504 filament segments, a yield of 69 percent of included segments. |
|---|---|
| Details | There are 4 helices of myosin heads, rotated 30 degrees, every 145 Angstroms. The filament segments were selected based on visual judgement of good helical order |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - #0 - Chain ID: A / Chain - #1 - Chain ID: B / Chain - #2 - Chain ID: C / Chain - #3 - Chain ID: D / Chain - #4 - Chain ID: E / Chain - #5 - Chain ID: F |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Situs 2.3 |
| Details | PDBEntryID_givenInChain. Protocol: Flexible Fitting. The flexible docking procedure is based on a connected (motion capture) network of identified features within the atomic model. The atomic model is allowed to move according to displacements tracked by 31 control points defined by the network, in order to find the best match to the cryo-EM map |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: Correlation |
| Output model |  PDB-3dtp:  PDB-3jbh: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller